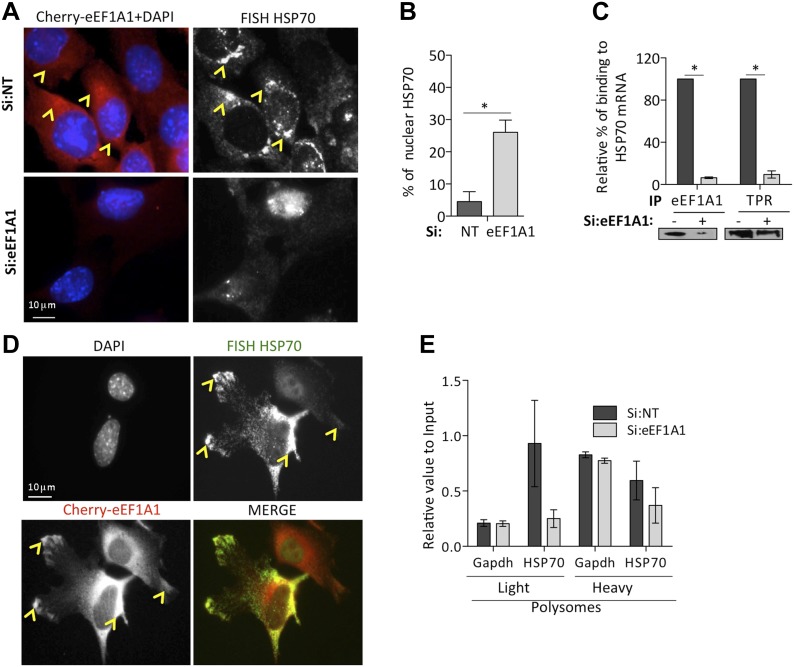
Figure 5. eEF1A1 is required for HSP70 mRNA export from the nucleus.
(A) eEF1A1 mediates HSP70 mRNA export upon HS. MEFs were infected with a lentivirus expressing Cherry-eEF1A1. eEF1A1 expression was knocked down by siRNA. At 120 min after HS cells were fixed and HSP70 mRNA detected by FISH. Nucleus stained with DAPI. Merged images show cherry-eEF1A1 in red and nucleus in blue. Gray image shows HSP70 mRNA FISH. Bar = 10 microns. (B) HSP70 mRNA retention in the nucleus of eEF1A1-knocked down cells. The plot shows total (T) and nuclear (N) HSP70 mRNA in control (Si:NT) or eEF1A1-knocked down cells after heat shock. RNA from HeLa cells was RT with random primers followed by quantification of GAPDH and HSP70 mRNAs by QPCR. Total or nuclear HSP70 mRNA was normalized to that of total GAPDH. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05. (C) Knock down of eEF1A1 suppresses binding of TPR1 to HSP70 mRNA. HSP70 mRNA was co-IPed with antibodies against eEF1A1 or TPR1 from heat-shocked HeLa cells knocked down of eEF1A1 or mock transfected. Total and IP RNA was RT with random primers and GAPDH and HSP70 mRNAs were quantified by QPCR. Total and IP HSP70 mRNA was normalized against total GAPDH mRNA. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM from three experiments. (D) MEFs were infected with a lentivirus expressing Cherry-eEF1A1. At 120 min of HS, cells were fixed and HSP70 mRNA detected by FISH. Nucleus stained with DAPI. Merged images show HSP70 FISH in green and cherry-eEF1A1 in red. Yellow arrowheads indicate areas with high density of HSP70 mRNA and brighter signal for cherry-eEF1A1. (E) eEF1A1 contributes to loading of HSP70 mRNA into polysomes. RNA collected from light and heavy polysome fractions was reverse-transcribed with random primers followed by quantification of GAPDH and HSP70 mRNAs by QPCR. Values relate to those obtained from total RNA (Input). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.