Figure 1.
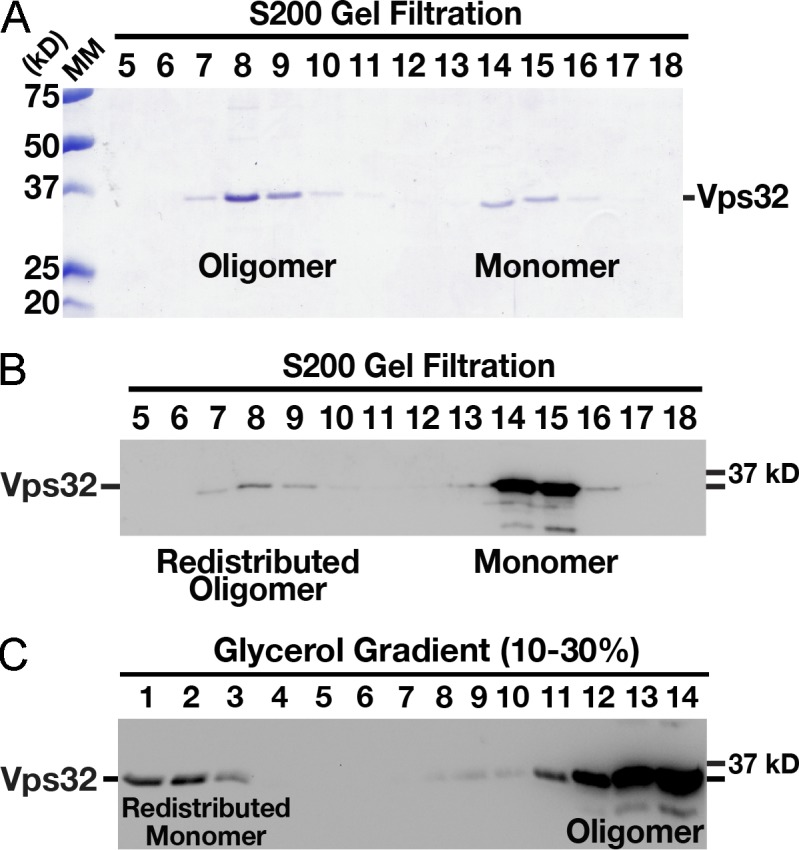
C. elegans Vps32 forms an exchangeable pool of monomers and oligomers in solution. (A) Coomassie-stained fractions of purified, recombinant C. elegans Vps32 after size exclusion chromatography and SDS-PAGE analysis. The monomer and oligomer peaks exhibit Stokes radii of 3.8 and 9.1 nm, respectively. (B) Immunoblot analysis using Vps32 antibodies demonstrating that a fraction of the monomer pool is redistributed to the oligomer pool after a second round of size exclusion chromatography. The monomer and oligomer peaks continue to exhibit Stokes radii of 3.8 and 9.1 nm, respectively. (C) Immunoblot analysis using Vps32 antibodies showing the distribution of recombinant Vps32 after fractionation over a glycerol gradient. The oligomer pool (fractions 7 and 8 recovered after size exclusion chromatography, as shown in A) was separated by velocity sedimentation. A redistributed monomer peak with a sedimentation value of 2.1 S is highlighted. Based on our hydrodynamic observations, the apparent molecular mass (MM) of Vps32 (monomer pool) is ∼33 kD (Siegel and Monty, 1966), similar to its predicted molecular mass of 25 kD, as determined by amino acid composition.
