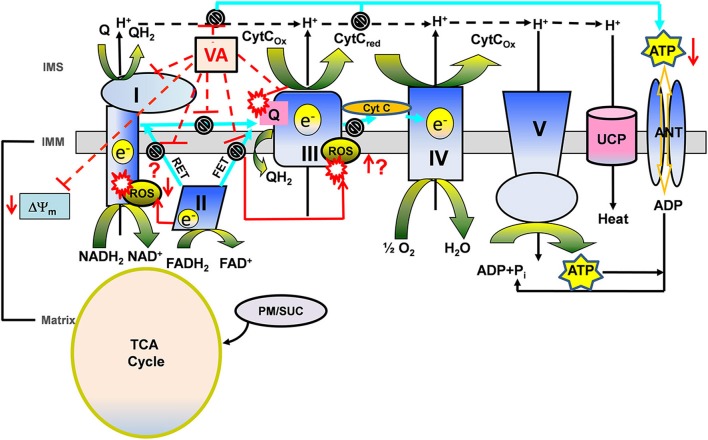
Figure 4.
A proposed view of cardioprotection based on the modulating effects of volatile anesthetics (VA) on electron transport chain (ETC) function in the presence of different substrates. Mitochondria generate reducing equivalents, NADH2 and FADH2, via the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle in the matrix during electron transfer through the ETC complexes of the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) to generate the proton gradient (H+) and mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm). The transfer of electrons through the ETC complexes to the final electron acceptor, O2, is coupled with the H+ gradient to phosphorylate ADP to ATP by ATP synthase (complex V). During electron transfer, attenuation of complex I and complex III generates O2 free radical anions (O·−2) leading to other ROS. Complex II mediates forward and reverse electron transfer (FET and RET, respectively), which generates ROS at complex I and complex III. VA modulate complex I and III, therefore affecting bioenergetics (ΔΨm, redox state, respiration, phosphorylation). During oxidation of complex II substrate succinate (Suc), ROS generated via RET may be considered “deleterious,” while ROS generated via FET by complex III inhibition may represent the “signaling” ROS. VA-induced complex I inhibition may decrease the generation of RET mediated “deleterious” ROS and could mediate the generation of “signaling” ROS at complex III. Whereas, during oxidation of complex I substrate pyruvate/malate (PM), VA-induced complex I inhibition could mediate generation of “signaling” ROS at complex I. VA-induced complex I and complex III inhibition may mediate slower rates of proton and electron transfer to reduce ATP synthesis during ischemia to preserve it during reperfusion. Possible modulating effects of VA on uncoupling protein (UCP) in promoting proton leak and uncoupling in cardioprotection are also noted. Other abbreviations: ANT, adenine nucleotide translocase; TCA cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle; IMS, inter mitochondrial space.