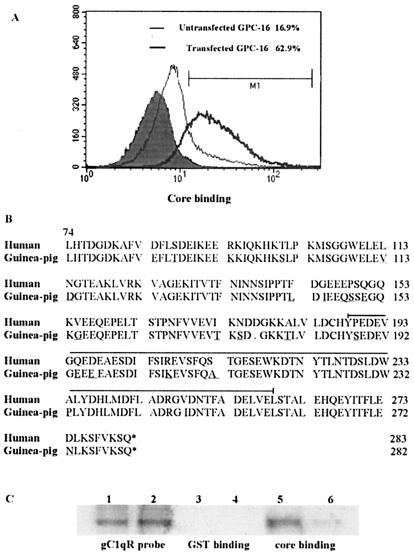
FIG. 3.
HCV core binding on GPC-16 cells is increased upon transfection with Hu-gC1qR. (A) HCV core binding on GPC-16 cells. GPC-16 cells, both untransfected (thin line) and stably transfected with Hu-gC1qR (thick line), were incubated with 2 μg of HCV core/ml at 37°C for 2 h. Core binding was determined by FACS analysis as described above. The percentages of cells that were positive for HCV core binding, relative to the isotype control (filled area), are shown. (B) Alignment of the cDNA-derived gC1qR sequences from humans and guinea pigs. Amino acid residues that diverge in humans and guinea pigs are underlined. A deleted amino acid at position 177 (D) is notated with a dot. The HCV core binding region of gC1qR is bracketed. This alignment was constructed by using DNA Strider. (C) Comparison of the relative HCV core binding abilities of Hu-gC1qR and guinea pig gC1qR by GST pull-down analysis. GST alone (lanes 3 and 4) or GST-core (lanes 5 and 6) was incubated with in vitro-translated Hu-gC1qR (lanes 1, 3, and 5) or guinea pig gC1qR(lanes 2, 4, and 6). After a pull-down reaction with glutathione-agarose beads, samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, and [35S]Met-labeled gC1qR was detected by autoradiography.