Figure 4.
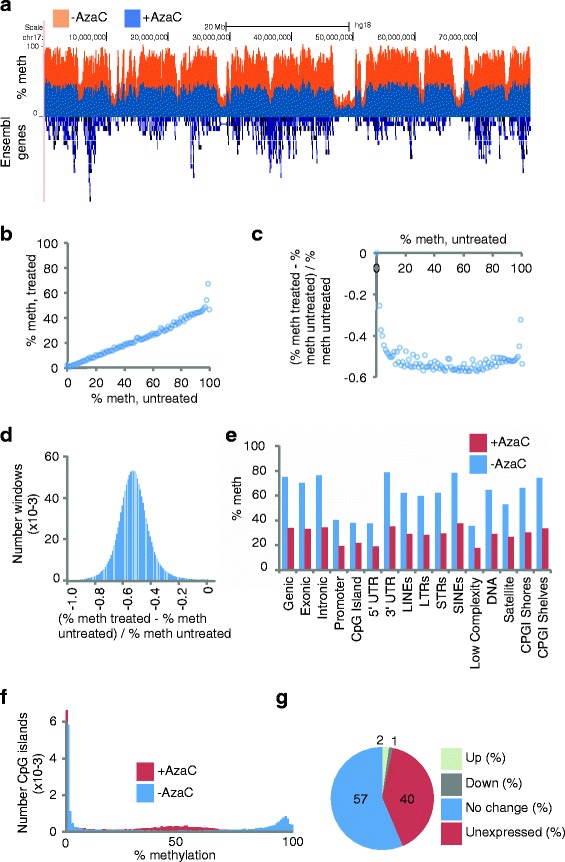
AzaC induces global DNA hypomethylation, but select changes in gene expression. (a) Representative bisulphite sequencing data for AzaC-untreated (orange) and treated (blue), and Ensembl genes (blue (below)) over chromosome 16. Percent methylation on y-axis. (b, c) Relationship between global average untreated methylation and treated methylation. Reference CpGs are placed into integer bins (in the range of 0 to 100) corresponding to AzaC-untreated% methylation. The mean AzaC-treated% methylation (b) and mean relative difference (c) are calculated for the CpGs in each bin, and plotted. (d) Distribution of methylation differences approximates a normal distribution. The genome is split into non-overlapping 2 kb windows, and the relative difference in methylation at CpGs calculated for each window. (e) Methylation changes within genomic features. Mean percentage methylation over specified genomic features, for AzaC-untreated (blue) and AzaC-treated (red) cells. (f) Methylation plotted for untreated and treated CpG islands. Histogram of percentage CpG methylation at CpG islands for AzaC untreated (blue) and AzaC treated (red) cells. (g) Classification of gene expression changes after AzaC treatment. Proportion of genes that are up- and downregulated (BH-fdr <0.05), unchanging (BH-fdr >0.05) and unexpressed in either sample (FPKM = 0). Up, 792; down, 426; no change, 20,385; unexpressed, 14,516. See Additional file 5: Dataset 1.
