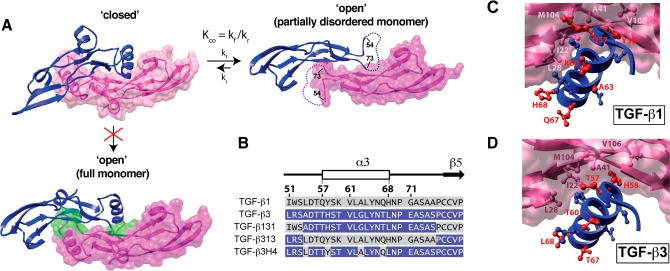
Figure 1.
Closed and open forms of TGF-β3 and construct design for this study. (A) Closed and open conformations of TGF-β3. Closed form is from the crystal structure of unbound TGF-β3 (PDB code 1TGJ), while the open form is from the crystal structure of the TGF-β3/TβRII complex (PDB code 1KTZ; TβRII not displayed). Open form differs from the closed by a 101° degree rotation of the monomers away from one another; the open form also has no electron density for the α-helix 3 and connecting loops (residues 55–72, dashed line). Disorder of α-helix 3 in the open form is likely caused by steric overlap between residues near the C-terminal end of α-helix 3 and the heel of the opposing monomer; this is shown by the structure below the “closed” form in which TGF-β3 monomers from the closed form (with an intact α-helix 3) have been overlaid onto the partial monomer structures of the open form. Steric clashes between α3 and the heel of one monomer and the other are highlighted in green. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of TGF-β1 and -β3 and the sequences of TGF-β131, TGF-β313 and TGF-β3H4. Secondary structural elements correspond to those from the crystal structure of TGF-β3 (PDB code 1TGJ). Residues from TGF-β1 are highlighted with a gray background, while those from TGF-β3 with a blue background; the same color scheme is used for TGF-β131, TGF-β313, and TGF-β3H4. (C, D) Interaction of α-helix 3 of one monomer with the heel of the other for the closed form of TGF-β1 and -β3 (PDB codes 1KLC and 1TGJ, respectively). Heel residues conserved between TGF-β1 and -β3 (L28, I22, M104, V106, and A41) are highlighted in light and dark pink. Helical residues that differ between TGF-β1 and -β3 are highlighted in red.