Figure 1.
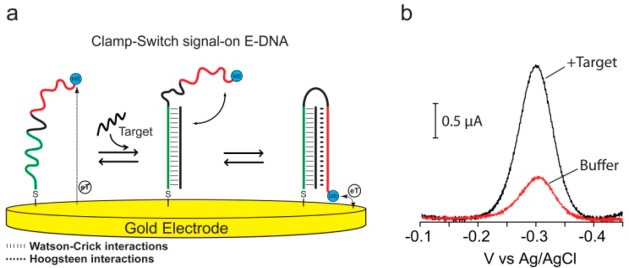
(a)Clamp-switch E-DNA sensor is composed of a DNA probe modified at its 3′-end with a methylene blue redox tag and at its 5′-end with a thiohexyl moiety for attachment on a gold electrode. The probe is designed with a first recognition element, a 15-base polypyrimidine portion (green portion) that can recognize a complementary target sequence via Watson–Crick base pairing. The second recognition element, a polypyrimidine sequence (red portion) can then fold back to form a triplex structure through Hoogsteen base pairing.4,13 This brings the redox label into close proximity with the electrode surface, increasing electron transfer efficiency and resulting in an increase in the observed current (b).
