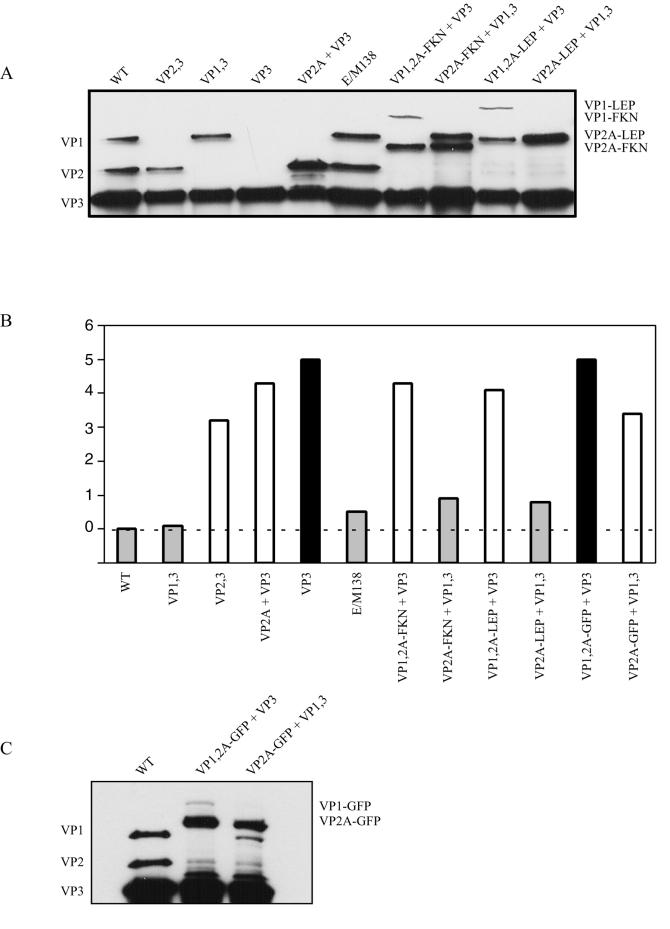
FIG. 7.
Capsid protein stoichiometry and infectivity of AAV virus stocks missing a capsid protein or containing a ligand insertion. (A) Western blot of virus stocks purified by use of iodixanol gradients and heparin sulfate column chromatography. Approximately 1011 AAV-like particles were separated by SDS-10% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and analyzed by Western blotting with the B1 antibody. WT, wild type. (B) Particle-to-infectivity ratios of AAV-like particles relative to that of pIM45. The particle-to-infectivity ratio for each particle was calculated by dividing the average genomic titer by the average FCA titer (see Material and Methods and Table 2). The particle-to-infectivity ratio for each type of virus was then normalized to that of wild-type virus (pIM45) by dividing the particle-to-infectivity of each AAV-like particle by the particle-to-infectivity of pIM45, and the log10 value of the ratio was plotted. The wild-type pIM45 ratio equals zero and is indicated by the dashed line. Grey bars, particles with infectivity comparable to that of pIM45 (within 1 log unit); white bars, particles with significantly reduced infectivity (1- to 4-log-unit-lower infectivity); black bars, particles that were essentially noninfectious (>4-log-unit-lower infectivity). (C) Western blot of approximately 1011 AAV-like particles with GFP inserted in the capsid. Virus samples were purified as for panel A above, fractionated by SDS-10% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and analyzed by Western blotting with the B1 antibody.