Figure 5.
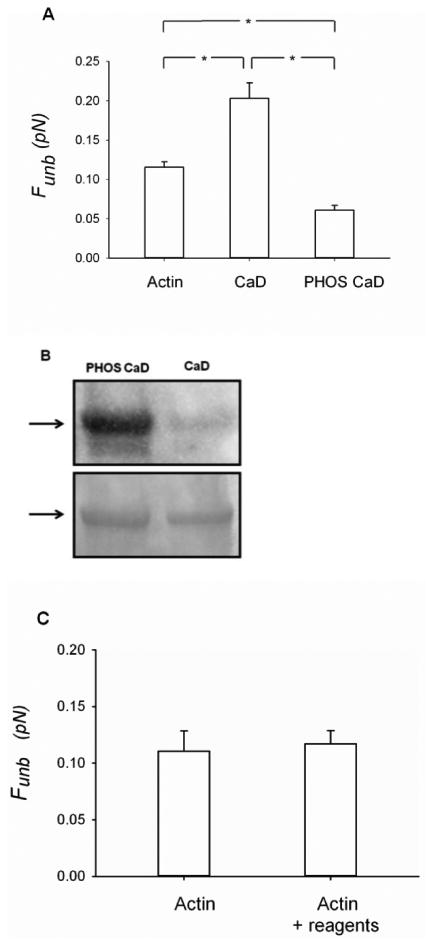
Effects of phosphorylated CaD on the unbinding force (Funb) of unphosphorylated myosin from actin. A) The measurements were performed with unregulated actin (1nM) filaments (N = 10), actin (1nM) filaments regulated by CaD (10nM) (N = 14) or actin (1nM) filaments regulated by ERK-phosphorylated CaD (10nM) (N = 10). The results are reported as average force per myosin head. CaD: caldesmon, PHOS CaD: phosphorylated caldesmon. *: p < 0.05. B) The phosphorylation of CaD was assessed by Western blotting (top panel). The total protein loading was assessed by Coomasie blue staining of the membrane (bottom panel). C) Effects of the CaD phosphorylating reagents on the unbinding force (Funb) of unphosphorylated myosin from actin, in the absence of caldesmon. The measurements were performed with unregulated actin (1nM) filaments (N=4) and with unregulated actin (1nM) filaments in the presence of the reagents used to phosphorylate CaD (see methods for details) (N=3).
