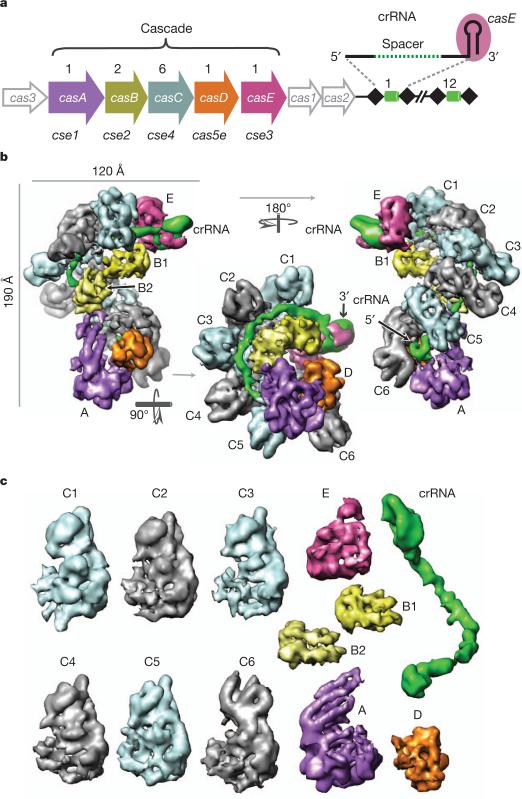
Figure 1. Structure of the Cascade complex from E. coli.
a The CRISPR system in E. coli K12 (Cse-type) consists of eight cas genes and a downstream CRISPR locus. casA to casE are members of large gene families, referred to as cse1, cse2, cse4, cas5e and cse3, respectively28,29. The CRISPR consists of a series of 29-nucleotide repeats (black diamonds) separated by 32-nucleotide spacer sequences (green cylinders). CasE (magenta) is an endoribonuclease that specifically binds to a stable stem–loop in the CRISPR RNA repeat and cleaves 8 nucleotides away from the spacer sequence in the 5′ direction9,11,14. b, Cascade assembles into a sea-horse-shaped architecture where the crRNA (green) is positioned along a helical arrangement of six CasC subunits (C1–6). The helical spine is capped at its ends by two prominent features that represent the head (E, CasE) and tail (A, CasA) of the sea-horse anatomy. D, CasD. c, Cascade consists of unequal numbers of Cas proteins and a crRNA (CasA1B2C6D1E1crRNA1). The first five CasC subunits (C1–5) are structurally similar, whereas CasC6 is distinct. B1, CasB1; B2, CasB2.