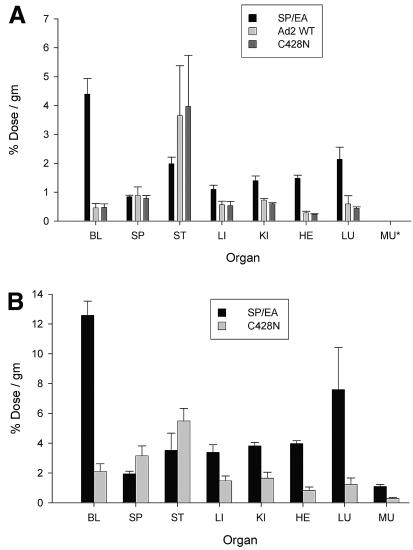
FIG. 4.
Biodistribution of radioiodinated Ad2 knob proteins. (A) Wild-type (WT) and mutant Ad2 knob proteins were directly labeled with 131I by the iodobead method (Pierce Biotechnology, Inc.), and then injected intravenously into mice (via the tail vein). After 6 h of circulation, mice were sacrificed, and the radioactivity in dissected organs was measured. BL, blood; SP, spleen; ST, stomach; LI, liver; KI, kidney; HE, heart; LU, lung; MU, muscle (data for muscles were not collected in the experiment shown). Wild-type and C428N mutant Ad2 knobs have equivalent CAR-binding activities, whereas the SP/EA mutant is unable to bind to CAR. Differences between radioactivity levels in organ samples from mice injected with wild-type versus C428N knob were not significant (P > 0.05). Significant differences (P < 0.05) in radioactivity levels in the blood, liver, kidneys, heart, and lungs were observed between mice injected with the non-CAR-binding SP/EA mutant and the CAR-binding wild-type or C428N knob. (B) The same experiment as that for which results are shown in panel A was performed, except that knob proteins were indirectly labeled with 125I by using the Bolton-Hunter reagent (6). Differences in radioactivity levels in organs from mice injected with SP/EA versus C428N knob were all significant (P < 0.05) except for levels in the stomach.