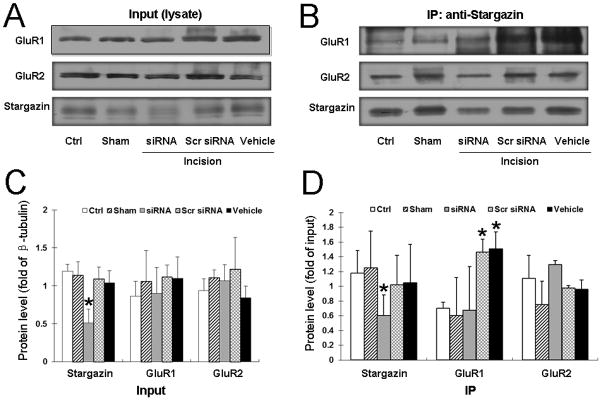
Fig. 7. Intrathecal pretreatment of rats with small interfering RNA (siRNA)311 prevents the increase in stargazin–GluR1 interaction after plantar incision.
Representative immunoblots illustrate (A) total GluR1 and GluR2 protein (Input) and (B) GluR1 and GluR2 coimmunoprecipitated by stargazin antibody (IP: anti-stargazin) in the ipsilateral dorsal horn tissue of different groups. (C) Quantitative analysis shows that intrathecal pretreatment with siRNA311 significantly decreased stargazin expression in the ipsilateral dorsal horn of rats at 3 h after plantar incision. The stargazin levels did not differ significantly among the other groups. The total GluR1 and GluR2 protein (Input) levels were not significantly different among the groups. (D) Coimmunoprecipitation results show that plantar incision significantly increased the interaction between stargazin and GluR1 in the dorsal horn compared to the level of interaction in the naïve control (Ctrl) and sham-operated groups. However, pretreatment with siRNA311 reduced the level of stargazin-GluR1 interaction such that it was no different from the level in the control and sham-operated groups. Stargazin–GluR2 interaction was similar in all groups. IP: immunoprecipitation; IB: immunoblotting; Scr siRNA, scrambled siRNA. *P < 0.05 compared to the control group. n = 6 rats per group.