Figure 6. Lithium attenuates the sevoflurane-induced GSK3β activation, Tau phosphorylation and elevation of IL-6 in hippocampus of mice.
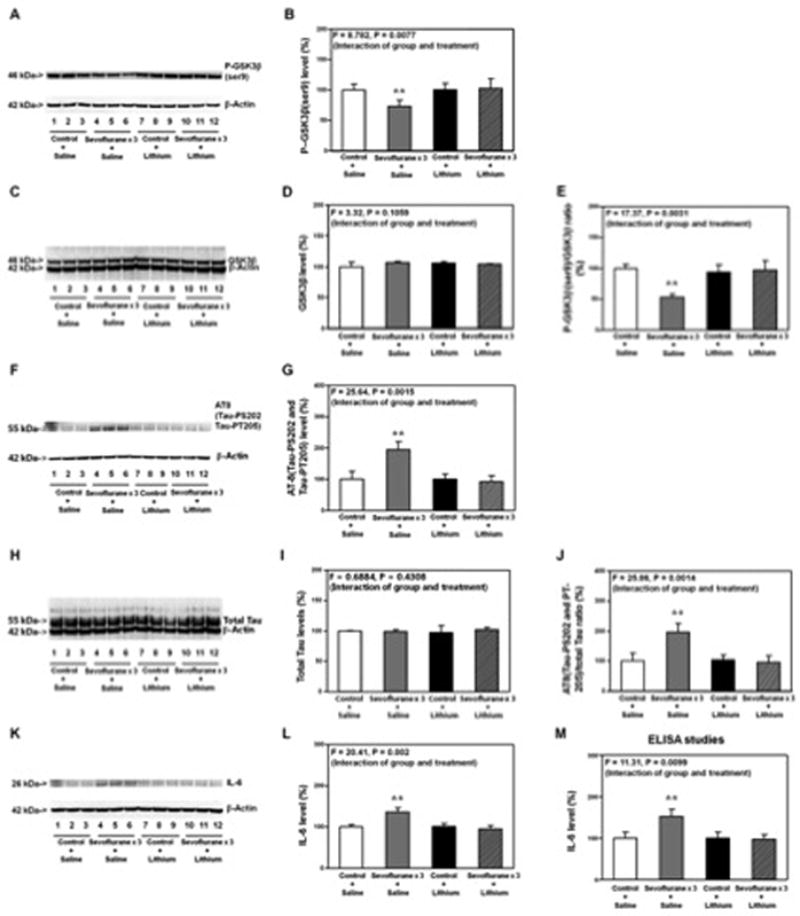
A. Anesthesia with 3% sevoflurane for two hours daily for three days reduces the levels of P-GSK3β(ser9) (lanes 4 to 6) as compared to control condition (lanes 1 to 3). Lithium treatment alone (lanes 7 to 9) does not alter the levels of P-GSK3β(ser9) as compared to control condition, but the lithium treatment (lanes 10 to 12) attenuates the sevoflurane-induced reduction in the P-GSK3β(ser9) levels (lanes 4 to 6). There is no significant difference in the β-actin levels among these treatments. B. Quantification of the Western blot shows that lithium (net bar) attenuates the sevoflurane-induced reduction in the P-GSK3β(ser9) levels (gray bar) (F = 8.782, P = 0.0077, Two-way ANOVA). There is no significant interaction of sevoflurane and lithium on the GSK3β levels (C and D). E. The quantification of the Western blots (A and C) shows that lithium attenuates the sevoflurane anesthesia-induced reduction in the ratio of P-GSK3β(ser9)/GSK3β (gray bar versus net bar, F = 17.37, P = 0.0031, Two-way ANOVA). F. Anesthesia with 3% sevoflurane for two hours daily for three days increases the levels of AT8(Tau-PS202 and Tau-PT205) (lanes 4 to 6) as compared to control condition (lanes 1 to 3). Lithium treatment alone (lanes 7 to 9) does not alter the levels of AT8 as compared to control condition, but the lithium treatment (lanes 10 to 12) attenuates the sevoflurane-induced increase in the AT8 levels (lanes 4 to 6). There is no significant difference in the β-actin levels among these treatments. G. Quantification of the Western blot shows that lithium (net bar) attenuates the sevoflurane-induced increase in the AT8(Tau-PS202 and Tau-PT205) levels (gray bar) (F = 25.64, P = 0.0015, Two-way ANOVA). There is no significant interaction of sevoflurane and lithium on the total Tau levels (H and I). J. The quantification of the Western blots (F and H) shows that lithium attenuates the sevoflurane anesthesia-induced increase in the ratio of AT8/total Tau (gray bar versus net bar, F = 25.86, P = 0.0014, Two-way ANOVA). K. Anesthesia with 3% sevoflurane for two hours daily for three days increases the levels of IL-6 (lanes 4 to 6) as compared to control condition (lanes 1 to 3). Lithium treatment alone (lanes 7 to 9) does not alter the levels of IL-6 as compared to control condition, but the lithium treatment (lanes 10 to 12) attenuates the sevoflurane-induced increase in the IL-6 levels (lanes 4 to 6). There is no significant difference in the β-actin levels among these treatments. L. Quantification of the Western blot shows that lithium (net bar) attenuates the sevoflurane anesthesia-induced increase in the IL-6 levels (gray bar) (F = 20.41, P = 0.002, Two-way ANOVA). M. ELISA studies show that lithium (net bar) attenuates the sevoflurane anesthesia-induced increase in the IL-6 levels (gray bar) (F = 11.31, P = 0.0099, Two-way ANOVA). P, phosphorylated; Tau-PS202, Tau phosphorylated at serine 202; Tau-PT205, Tau phosphorylated at threonine 205; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; ser9, serine 9; IL-6, interleukin-6; ANOVA, Analysis of Variance. N = 6 in each group.
