Figure 7. Lithium mitigates the sevoflurane-induced cognitive impairment in young mice.
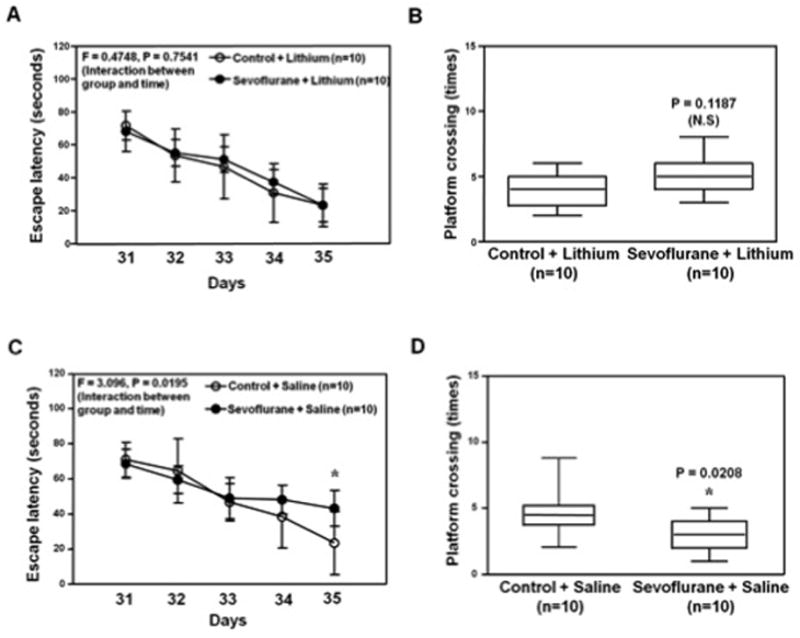
A. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measurement analysis shows that there is no statistically significant interaction of treatment and group based on the escape latency of MWM between the control plus lithium (N = 10 in each group) and sevoflurane (3% for two hours daily for three days) plus lithium (N = 10 in each group) treated mice. B. The Mann-Whitney test shows that there is no significant difference in platform crossing times of mice swimming in the MWM between the control plus lithium (N = 10 in each group) and sevoflurane plus lithium treatments (N = 10 in each group). C. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measurement analysis shows that there is statistically significant interaction of treatment and group based on escape latency of MWM between the control plus saline (N = 10 in each group) and sevoflurane (3% for two hours daily for three days) plus saline (N = 10 in each group) treated mice (F = 3.096, P = 0.0195). The post-hoc (Bonferroni) test shows that the mice following sevoflurane plus saline has longer escape latency than the mice following control plus saline treatment at day P35. D. The Mann-Whitney test shows that the mice following sevoflurane plus saline (N = 10 in each group) have less platform crossing times than the mice following control plus saline (N = 10 in each group) in the MWM test. MWM, Morris Water Maze; ANOVA, analysis of variance.
