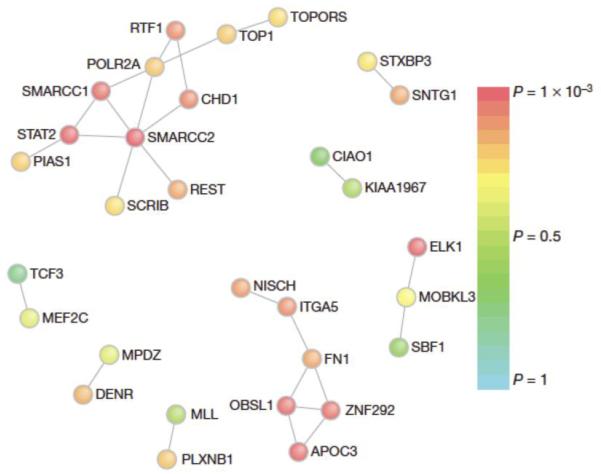
Figure 5. De novo exome mutations reveals a significant chromatin remodeling network in autism spectrum disorders.
Genes that harbor de novo mutations in patients with sporadic autism spectrum disorders, significantly interact at the level of proteins, revealing a chromatin remodeling network (the sub network including SMARCC2). Proteins are colored based on the significance of their interactions with other proteins in which de novo mutations were found as determined by the DAPPLE algorithm using protein interactions from InWeb. Figure is reproduced from 81 with permission.