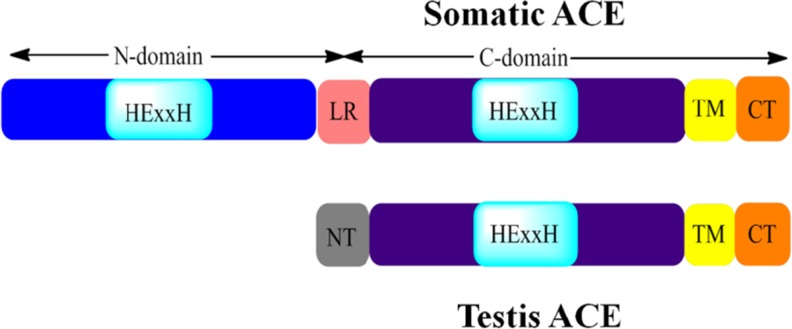
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the domain structures of sACE and tACE. sACE consists of two homologous domains: the N- and C-domains. Both contain a functional active site, illustrated here by the HExxH zinc binding motif. The two domains are joined by a short linker sequence (LR) which is unique to sACE. The N-domain and most of the C-domain are extracellular. There is a transmembrane (TM) domain towards the C-terminus of sACE followed by the C-terminus (CT) which is intracellular. In contrast, tACE is a single domain protein with only one active, shown here by a single HExxH zinc binding motif. The 36 residues at the N-terminus (NT) of tACE are unique, taking the place of the linker region (LR) in sACE. Like sACE, most of tACE is extracellular with a transmembrane domain (TM) and the C-terminus (CT) is positioned inside the cell