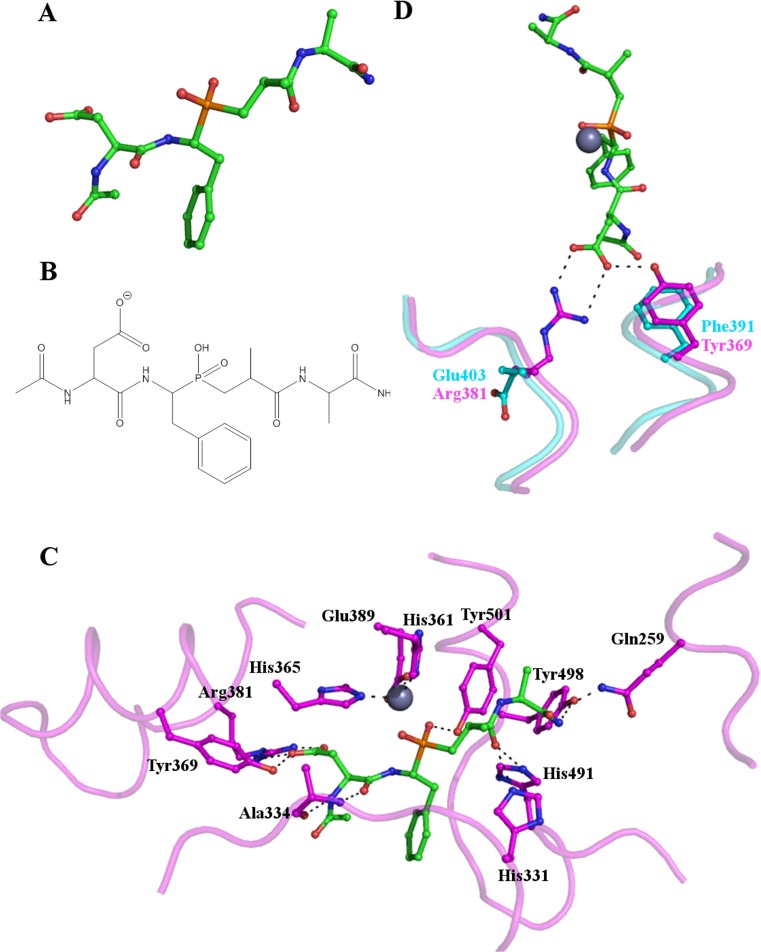
Fig. 5.
RXP407 binding to the N-domain of human sACE. (a) and (b) the structure of the phosphinic peptide N-domain selective ACE inhibitor RXP407. (c) Key residues involved in the binding of RXP407 to the active site of the N-domain of human sACE are shown as sticks with their carbon atoms in magenta. RXP407 is also shown as sticks, with green carbon atoms and the essential zinc is shown as a grey sphere. (d) Two key differences between the N- and C-domain active sites which are likely to affect RXP407 binding. In the C-domain Arg381 (magenta) is replaced by Glu403 (cyan) resulting in the loss of an interaction with the inhibitor. Similarly, Phe391 (cyan) in the C-domain is unable to hydrogen bond with RXP407 as Tyr369 (magenta) is in the N-domain