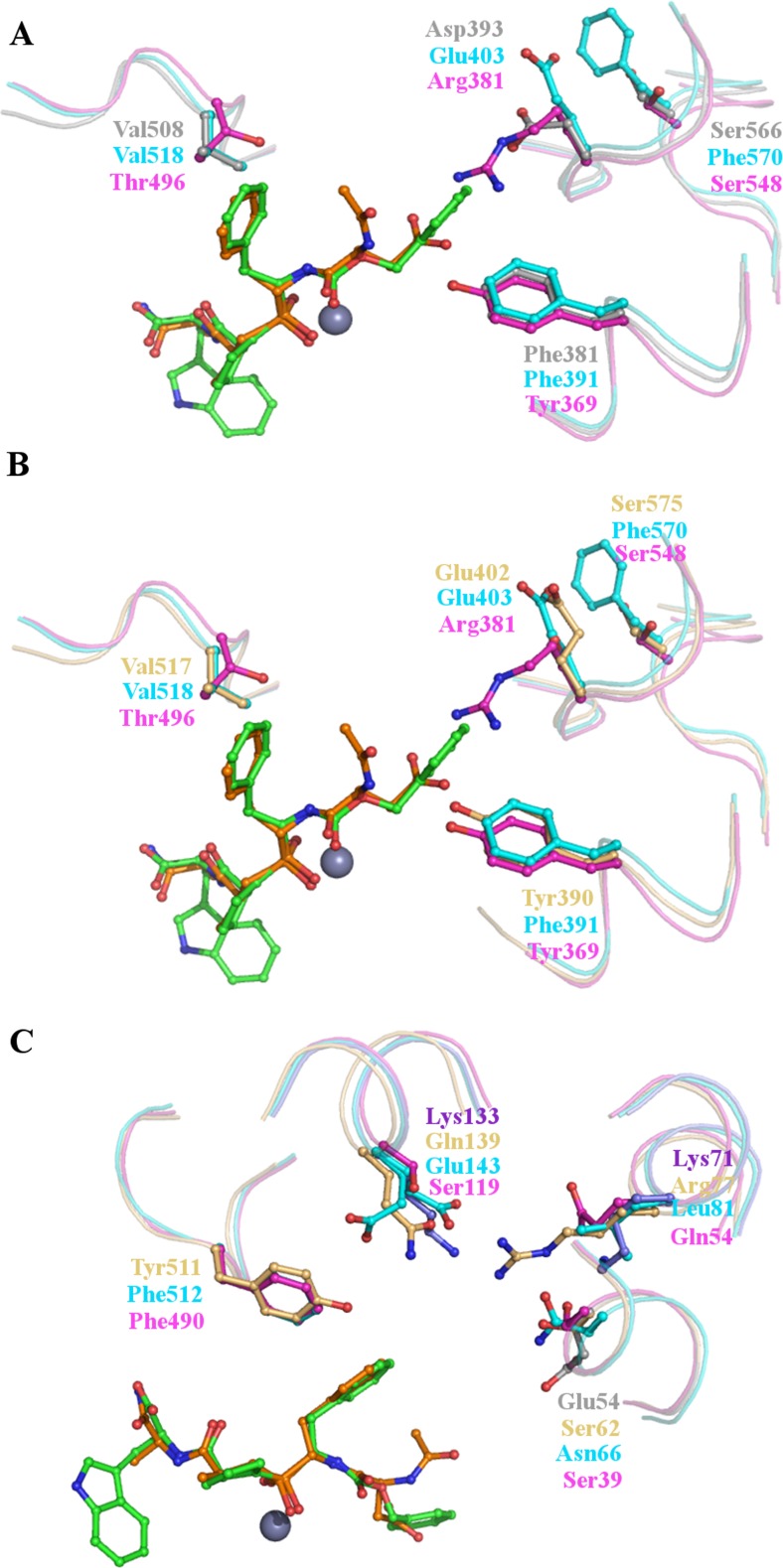
Fig. 7.
Features of the active sites of the AnoACE2-6 models compared to the N- and C-domains of human sACE. In all images the N-domain selective inhibitor RXP407 is shown as sticks with green carbon atoms and the C-domain selective inhibitor RXPA380 as sticks with orange carbon atoms. The catalytic zinc ion is a grey sphere. (a) The S2 subsite of AnoACE5 and 6. Key residues of AnoACE5 and 6 are shown as grey sticks using AnoACE5 numbering. The C-domain is shown as cyan sticks and the N-domain magenta. AnoACE5 and 6 share a conserved phenylalanine (Phe381) with the C-domain which is replaced by a tyrosine in the N-domain. This residue makes important contacts with the domain selective inhibitors and so suggests that AnoACE5 and 6 may share some binding preferences with the C-domain. There is also a conserved negative charge, Asp393 which is replaced by positive Arg381 in the N-domain, and a conserved valine, Val508, replaced by Thr496 in the N-domain. There is some similarity with the N-domain though, for example Ser566 which is replaced by Phe570 in the C-domain. (b) The S2 subsite of AnoACE2-4. The S2 subsites of the AnoACE2-4 models are very similar and so are represented here by AnoACE3a, shown as light orange sticks. There are some features shared with both the N- and C-domains of sACE; Tyr390 is conserved in the N-domain, but replaced by Phe391 in the C-domain, whilst Glu402 is conserved in the C-domain but replaced by the positive Arg381 in the N-domain. These residues are likely to have significant effects on substrate and inhibitor binding properties. (c) The S1 subsite of AnoACE2-6. Common features of the AnoACE2-6 models are represented by AnoACE3a in light orange, with unique features of AnoACE4 and AnoACE5 and 6 shown as violet and grey sticks respectively. The AnoACE2-6 models share a conserved tyrosine at Tyr511 which is replaced by phenylalanine in both the N- and C-domain. All of the models have a unique positively charged residue not found in the N- or C-domains, shown here by Lys71 in AnoACE4 and Arg77 in AnoACE3. AnoACE4 has a further positively charged residue, Lys133, which is replaced by neutral or negatively charged residues in the N- and C-domains and the other models. In contract AnoACE5 and 6 have an additional negative charge introduced by Glu54. These substitutions of charged residues are likely to have a significant effect on substrate and inhibitor binding properties