Figure 6. Transplanted allogeneic differentiated NPCs.
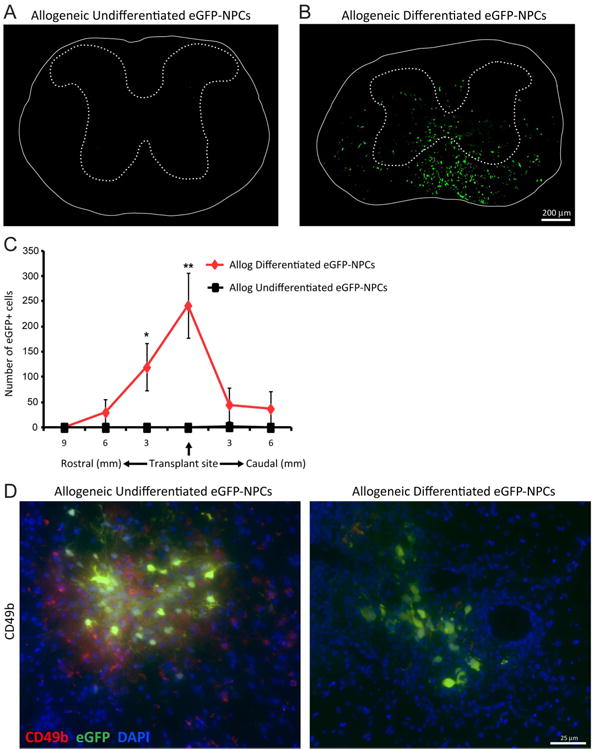
display increased survival following transplantation. Undifferentiated and differentiated eGFP-NPCs were transplanted into BALB/c mice (allogeneic transplant) on day 14 post-JHMV-infection. Representative coronal spinal cord sections of the transplant site from JHMV-infected mice receiving allogeneic undifferentiated eGFP-NPCs (A) or allogeneic differentiated eGFP-NPCs (B). Experimental mice were sacrificed at day 21 p.t. and migration and/or survival of transplanted cells evaluated by visualization of eGFP-expression from transplanted cells. (C) eGFP-NPCs were counted in coronal sections 9mm rostral and 6mm caudal to transplant site at 3mm intervals from mice transplanted with undifferentiated (n=4) or differentiated (n=6) eGFP-NPCs. Increased numbers of eGFP-NPCs (*p<0.05, **p=0.01) were present within the spinal cords of mice transplanted with differentiated eGFP-NPCs compared to undifferentiated allogeneic NPCs. (D) Representative immunofluorescence images showing CD49b+ NK cells (red) and eGFP-NPCs (green) with DAPI-stained nuclei (blue) at day 8 p.t. in coronal sections of spinal cords from mice transplanted with undifferentiated and differentiated allogeneic eGFP-NPCs.
