Figure 7. JHMV-infection increases RAE-1 expression on NPCs and elevates susceptibility to NK cell mediated lysis.
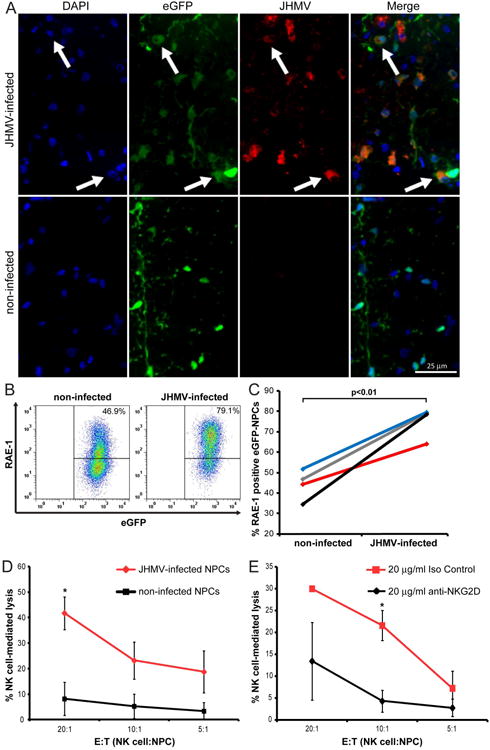
(A) Representative immunofluorescence images revealing co-localization (white arrows) of JHMV (spike protein; red) with eGFP (green) and DAPI-stained nuclei (blue) at day 7 p.t. in coronal sections of spinal cords from JHMV-infected (top panels) and non-infected (bottom panels) SCID mice transplanted with allogeneic eGFP-NPCs. (B) Cultured eGFP-NPCs were infected with JHMV (0.1 moi) for 24 hr and RAE-1 expression determined by flow cytometry. Representative flow analysis for RAE-1 expression on non-infected or JHMV-infected eGFP-NPCs is shown. (C) Paired data from four independent experiments showing increased (p<0.01) RAE-1 expression following JHMV infection. Each line represents and individual experiment. (D) Non-infected (black line) and JHMV-infected (red line) eGFP-NPCs were cultured with allogeneic NK cells in an LDH assay and the percentage of NK cell-mediated lysis at three different E:T ratios is shown. Data represent five independent experiments; *p<0.05. (E) JHMV-infected eGFP-NPCs were cultured with allogeneic NK cells plus 20 μg/ml anti-NKG2D (black line) or 20 μg/ml isotype-matched control Ig (red line) in an LDH assay and the percentage of NK cell-mediated lysis at three different E:T ratios is shown. Data represents three independent experiments; *p<0.05.
