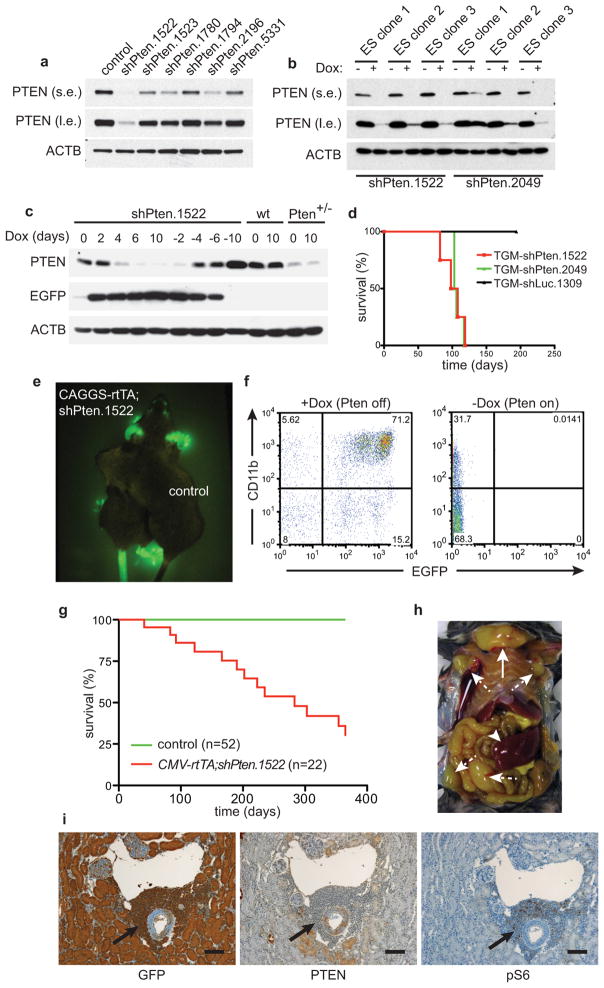
Extended Data Figure 1. Pten shRNA-transgenic mice enable conditional expression of PTEN and develop tumors after prolonged PTEN knockdown.
a, Western blot (WB) analysis of PTEN protein knockdown in NIH 3T3 cells infected with different Pten shRNAs at low multiplicity of infection. (s.e.: short exposure, l.e.: long exposure). b, PTEN protein knockdown assessed by WB in ES cell clones targeted with two different Pten shRNAs, either treated with doxycycline (Dox) or left untreated. c, MEFs from Rosa26-rtTA;shPten.1522 transgenic mice, wild type control mice, or Pten+/− mice were treated with Dox for the indicated times and analyzed for PTEN, GFP, and ACTB expression by WB. d, Overall survival of mice receiving bone marrow cells from tTA-transgenic mice infected with an inducible TRE-GFP-miR30 (TGM) retroviral vector expressing shPten.1522, shPten.2049 or control after irradiation with 600 rad. e, Fluorescence image of a CAGGS-rtTA;shPten.1522 mouse on Dox for 5 days and a CAGGS-rtTA only control mouse. f, Flow cytometric analysis of the peripheral blood of a CAGGS-rtTA;shPten.1522 mouse on Dox and an off Dox control mouse for myeloid (CD11b) and GFP marker expression 10 days after initiating Dox food. g, Overall survival curve of CMV-rtTA;shPten.1522 double-transgenic and control mice (single transgenic shPten.1522 or CMV-rtTA). Dox treatment for shRNA induction was started after weaning (at ~4 weeks of age). h, Situs of a tumor-bearing CAGGS-rtTA;shPten.1522 double-transgenic mouse. A large thymic tumor (full arrow), as well as enlarged lymph nodes (dashed arrows) and spleen (arrowhead), are visible. i, Immunohistochemical staining of kidney sections from a CAGGS-rtTA;shPten.1522 mouse for the indicated antigens. Arrows highlight a tumor infiltrate around a kidney venule. Scale bars show 100 μm.