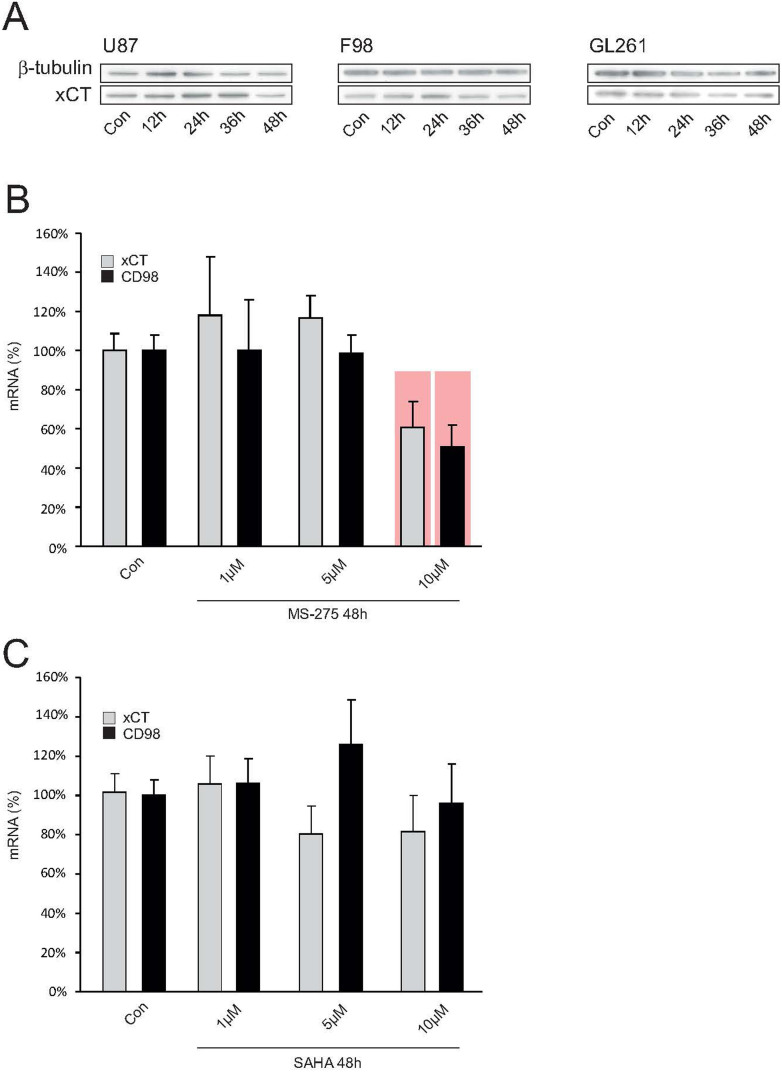
Figure 3. HDAC inhibitor SAHA acts specifically on xCT expression.
(A), The HDAC-inhibitor MS-275 does not affect xCT expression. MS-275 is a specific inhibitor of HDACs class I and was further evaluated for its ability to silence xCT-expression by Western blot. No regulation of xCT-expression was observed after treatment with MS-275 in the cell lines human U87MG, rat F98 and mouse GL261. Membranes were reprobed for β-tubulin expression to show that similar amounts of protein were loaded in each lane. The cropped blots are shown in the figure and the full-length blots are presented in supplementary figure 2. (B), MS-275 affects xCT in healthy brain tissue. The effect of MS-275 was also analyzed in healthy brain slice-cultures from rat with real-time RT-PCR. Here, only at 10 μM MS-275 a significant suppression of xCT and CD98 could be detected. (C), SAHA does not challenge xCT expression in healthy brain tissue. To further investigate the specificity with which the HDAC-inhibitor SAHA selectively modulates tumor cells and whether it incurs any adverse effects in healthy brain tissue, slice-cultures from healthy rat brains were treated with SAHA and the xCT- and CD98-expressions were analyzed again with real-time RT-PCR. No significant changes in xCT-expression were detectable. Thus, SAHA selectively changes xCT-expression in malignant gliomas, while healthy brain parenchyma remains unaffected by this HDAC-inhibitor. Statistical significance is calculated with the Student's t-test (mean ± s.d., *P < 0.05, n ≥ 8 per group).