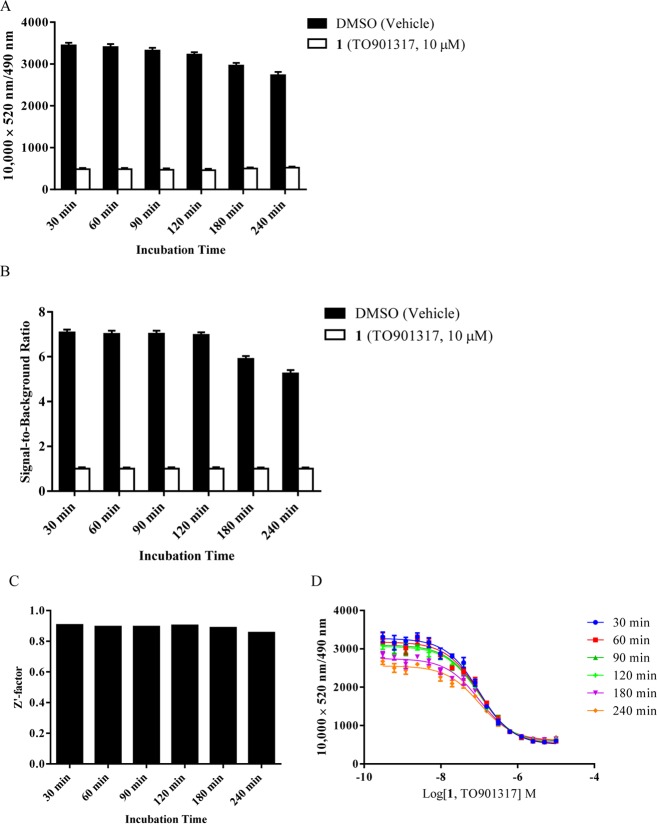
Figure 9.
Longitudinal signal stability of the interaction of 100 nM BODIPY FL vindoline (20) with 5 nM GST-hPXR-LBD and 5 nM Tb-anti-GST. (A) Interaction of 100 nM BODIPY FL vindoline (20) with 5 nM GST-hPXR-LBD and 5 nM Tb-anti-GST at the indicated time points in the presence of DMSO or TO901317 (1, 10 μM). (B) Signal-to-background ratio of the interaction of 100 nM BODIPY vindoline (20) with 5 nM GST-hPXR-LBD and 5 nM Tb-anti-GST at the indicated time points. (C) Z′-factor values of the interaction of 100 nM BODIPY FL vindoline (20) with 5 nM GST-hPXR-LBD and 5 nM Tb-anti-GST at the indicated time points. The Z′-factor was calculated from the total binding signal (DMSO) and background binding signal (10 μM TO901317) by using eq 2 (see Biology section). (D) TO901317 (1) dose–response curves in the presence of 100 nM BODIPY FL vindoline (20), 5 nM GST-hPXR-LBD, and 5 nM Tb-anti-GST at the indicated time points. For each time point tested in both panels A and B, the difference between DMSO and TO901317 (1, 10 μM) was substantial and statistically significant (p < 0.0001).