Figure 4.
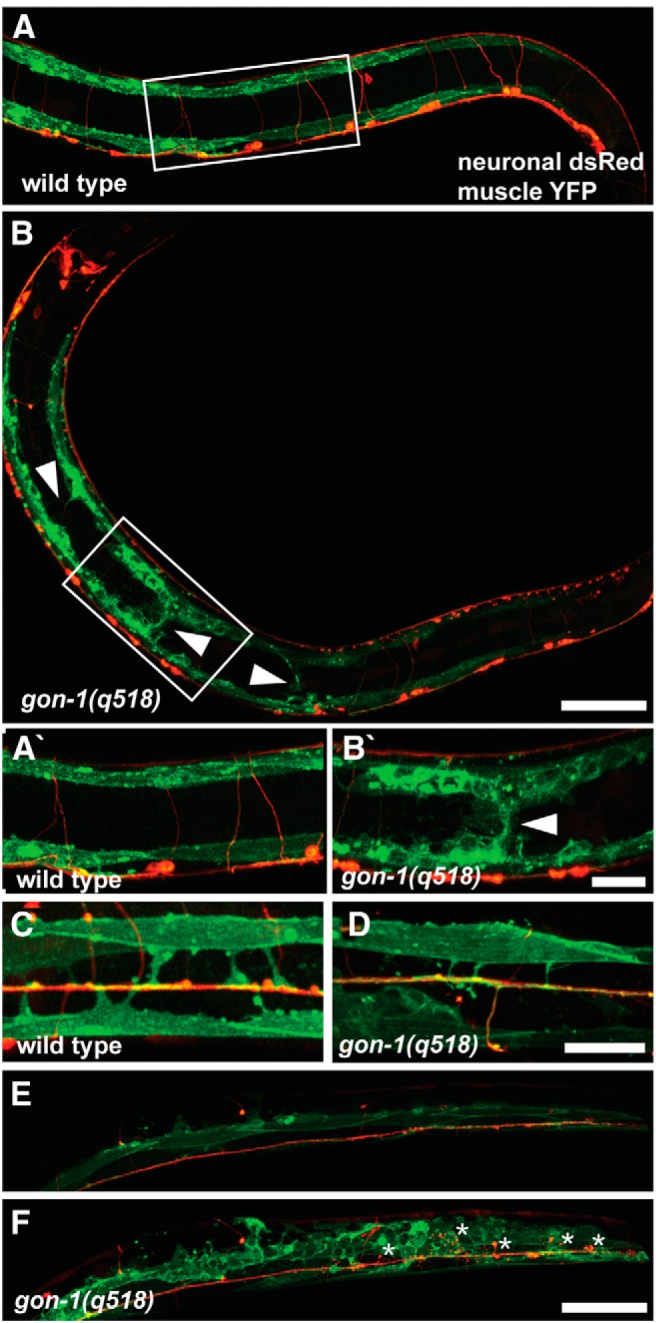
gon-1 mutants exhibit gross muscle overgrowth. A, In wild-type worms muscles (green) are restricted to the dorsal and ventral sides and never extend into the middle of the body. B, In contrast, in gon-1(q518) mutants, muscles are disorganized and extend into the body wall cavity (arrowheads). Boxes in A and B indicate areas magnified in A′ and B′. C, Dorsal view of a wild-type worm showing early born muscles arms (green) extending to the dorsal cord (red). D, Dorsal view of gon-1(q518) showing that early born muscle arms still form, although they are often slightly thinner than normal. E, Z-projection of superficial confocal sections from a dorsal view of a gon-1(q518) mutant, showing normal axonal and muscle morphology. F, Deeper confocal sections from the same worm reveal axonal protrusions (in red, asterisks) as well as the surrounding abnormal muscle morphology (in green). Worm shown in E and F has increased muscle GFP expression (wyEx5356 transgene, see Materials and Methods) for better visualization of the posterior muscles. Scale bars: A, B, E, F, 50 μm; A′, B′, C, D, 20 μm.
