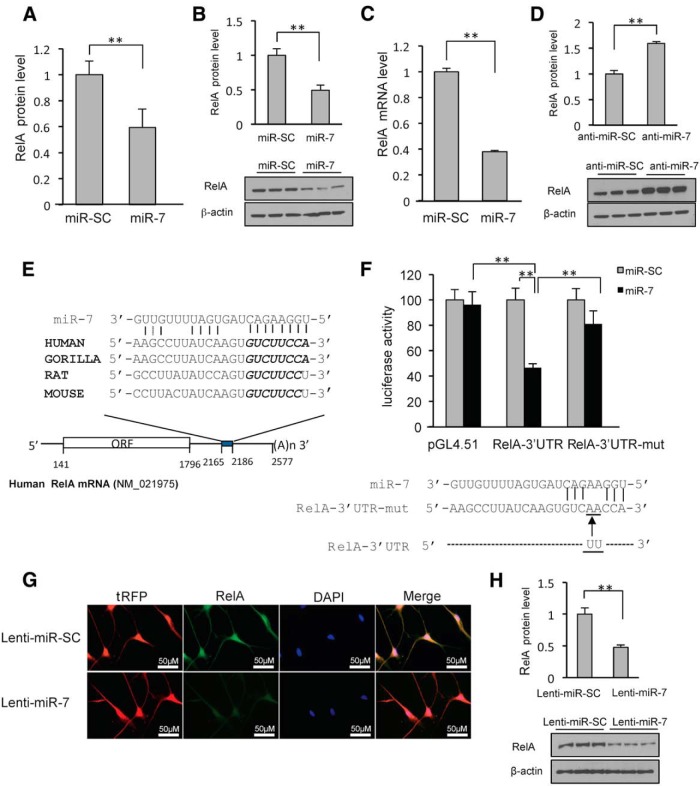
Figure 3.
MiR-7 targets the 3′-UTR of RelA mRNA. miR-7 reduces endogenous RelA levels in SH-SY5Y and differentiated ReNcell VM cells. A, Proteomics data. B, A representative Western blot using anti-RelA antibody is shown for triplicate samples in SH-SY5Y cells. C, Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of RelA mRNA in SH-SY5Y cells transfected with pre-miR-SC or pre-miR-7. Relative mRNA expression levels were normalized to GAPDH mRNA and are shown as a ratio compared to miR-SC. D, Western blot analysis showing that miR-7 inhibitor leads to accumulation of RelA. SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with 50 nm anti-miR-7 or control for 24 h for triplicate samples. E, Schematic diagram of RelA mRNA containing the predicted conserved binding site for miR-7. The seed match is presented in italic. F, Reporter gene assay using RelA-3′-UTR and its mutant form. SH-SY5Y cells were cotransfected with pre-miR7 or pre-miR-SC along with a luciferase construct harboring the 3′-UTR and pSV-β-galactosidase, and were harvested 24 h later. Luciferase activity was normalized against β-galactosidase activity. Bottom, Mutant RelA-3′-UTR sequence. G, Differentiated ReNcell VM cells were transduced with lenti-miR-7 or lenti miR-SC. RelA expression is detected as green fluorescence and lenti-miR-7-infected cells are detected as red fluorescence. Note that lenti-miR-7-infected cells have decreased RelA expression compared with lenti-miR-SC. H, Western blot analysis showing that lenti-miR-7 infection leads to decreased expression of RelA in differentiated ReNcell VM cells. **p < 0.01.