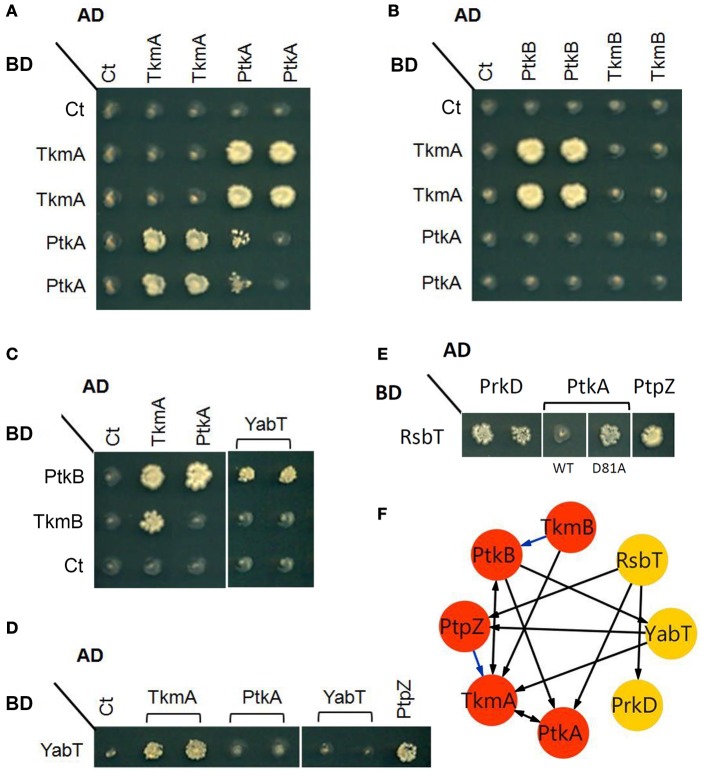
Figure 1.
Protein-protein interactions between some components of the tyrosine and serine/threonine signal transduction pathway. Interaction phenotypes were monitored by the ability of the yeast cells co-expressing a given bait (Gal4 BD-fusion) and prey (Gal4 AD-fusion) pair of proteins to grow on selective media, as described in the experimental procedures. (A) Reciprocal interactions between PtkA and its cognate modulator TkmA (fused to either AD or BD). (B) Interactions among components of the two BY-kinase systems: PtkA/TmkA (fused to BD) and PtkB/TkmB (fused to AD). (C–E) Examples of interactions between different families of kinases: (C) In addition of TkmA (here as positive control), PtkB (fused to BD) interacts with PtkA and YabT (fused to AD). (D) YabT (fused to BD) interacts with TkmA and PtpZ (fused to AD). (E) RsbT (fused to BD) interacts PrkD, PtpZ and catalytically inactive PtkA (D81A) (fused with AD). (F) A graphical representation of the interactions revealed by yeast two-hybrid. Proteins (nodes) are linked by edges (arrows) directed from bait to prey. Blue edges indicate additional interactions found after yeast two-hybrid screenings of the B. subtilis genomic library (Shi et al., unpublished results).