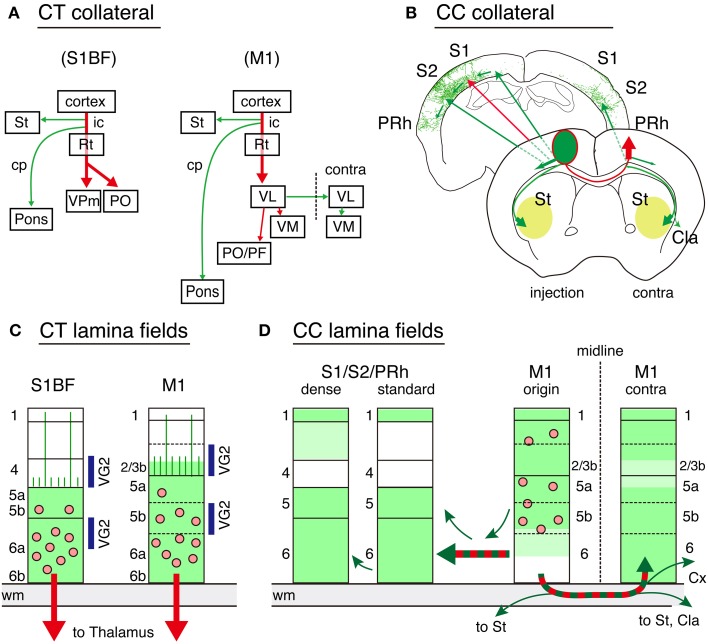
Figure 9.
Schematic representations of CT and callosal connectivity. The results of the double infection data for CT and callosal cell labeling are summarized. In all the panels, the red arrows indicate the targeted pathways specified by the TET double infection, while the green arrows indicate the adjunct collaterals labeled together. (A) Global collateral projection patterns for CT cells in S1BF and M1 are shown. The dotted line for M1 indicates the midline. (B) Global collateral projection patterns for callosal cells. The two coronal planes are shown as representatives. The frontal plane represents the projection from the soma to the contralateral M1 and the trajectories for collateral branches. The corticostriatal collaterals proceed bilaterally at this plane to enter from the lateral sides of the striatum to spread anteriorly and posteriorly (pale green). The ipsilateral corticocortical projections proceed caudolateraly within the cortex through layer 6 to S1, S2, and perirhinal cortices. The posterior plane shows the manual tracing of Figure 7F as a representative trajectory. (C) The local spread of processes (including both axons and dendrites) for CT cells is shown by green color. The pink dots represent the cell bodies. Layers 1 through 4 are mostly devoid of CT processes except the dendrites and axons that reach layer 1, which stem from layer 5 CT cells, or those that span layer 4 with few branching. These vertical processes are represented as vertical lines in panel (C). The layers with abundant thalamocortical terminations (VG2) are indicated by blue bars on the sides. (D) The local spread of processes for callosal cells in M1 (M1 origin) as well as the axonal terminations in the remote cortex are shown by green color. We observed two types of innervations in S1. In the dense region, we observed vertical extensions of the collaterals in layers 2 and 3, whereas a wide area of other S1 (standard) had collateral branches in various directions in layers 1, 5, and 6. Cla, claustrum; Cx, cortex; cp, cerebral peduncle; ic, internal capsule; PRh, perirhinal cortex; Rt, reticular thalamic nucleus; St, striatum; VL, ventrolateral thalamic nucleus; VM, ventromedial thalamic nucleus; VPm, ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus; PF, parafascicular thalamic nucleus; PO, posterior thalamic nuclear group.