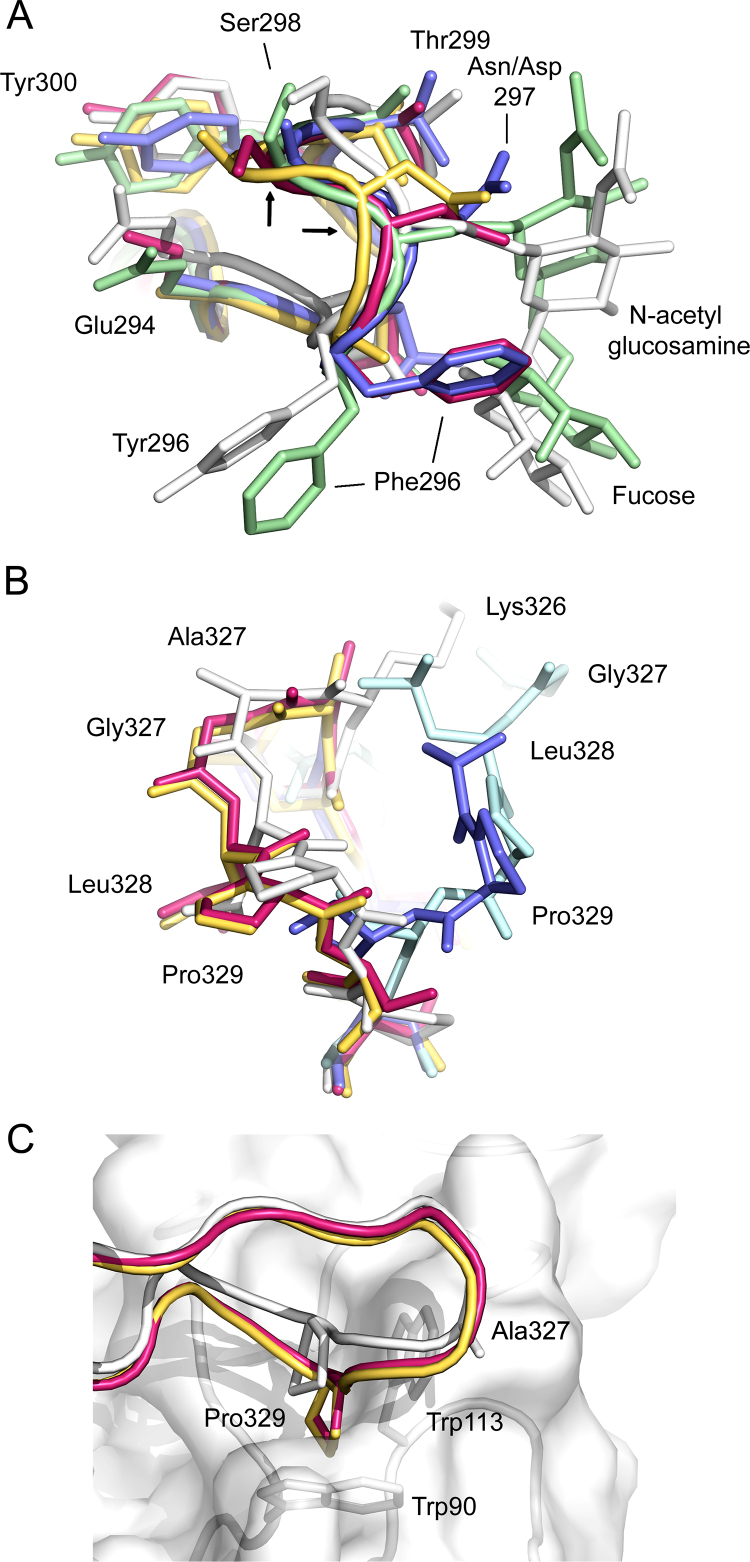
Fig. 3.
CH2 domain DE and FG loops. (A) The DE loop is shown for glycosylated IgG1-Fc (white) (PDB accession number 3AVE; Matsumiya et al., 2011) and glycosylated IgG4-Fc (green) (PDB accession number 4C54; Davies et al., 2014). For both glycosylated structures, the fucose residue, and the first N-acetyl glucosamine residue to which it is attached, is shown. Chains A (yellow), B (pink) and C (blue) from the degly-Fc structure are shown. The positions of the Cα atoms for residues 297 and 298 are indicated with arrows. The conformation adopted by Phe296 in molecules B and C from the degly-Fc structure clashes with the fucose residue, in contrast to the conformation adopted by Phe296 from glycosylated IgG4-Fc and Tyr296 from glycosylated IgG1-Fc, which does not. (B) The FG loop is shown for glycoslated IgG4-Fc, glycosylated IgG1-Fc and chains A-C from the degly-Fc structure. The FG loop for chains A and B from the degly-Fc structure (pink, yellow) adopt a similar conformation to the conserved loop conformation found in IgG1-Fc (white). The FG loop from molecule C (dark blue) is partially disordered, but the ordered residues adopt a similar conformation to that found in glycosylated IgG4-Fc (light blue). (C) The “proline sandwich” interaction between IgG-Fc and FcγRIII. The CH2 FG loop from IgG1-Fc (white) interacts with the Fcγ receptor (white), and the proline sandwich comprises Pro329 (IgG1-Fc) flanked by Trp90 and Trp113 (FcγRIII) (PDB accession number 3AY4; Mizushima et al., 2011). The CH2 FG loop is shown for chains A (yellow) and B (pink) from the degly-Fc structure. While the loop adopts a similar overall conformation to that in IgG1-Fc, the position of Pro329 is shifted in a manner that would clash with the receptor. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)