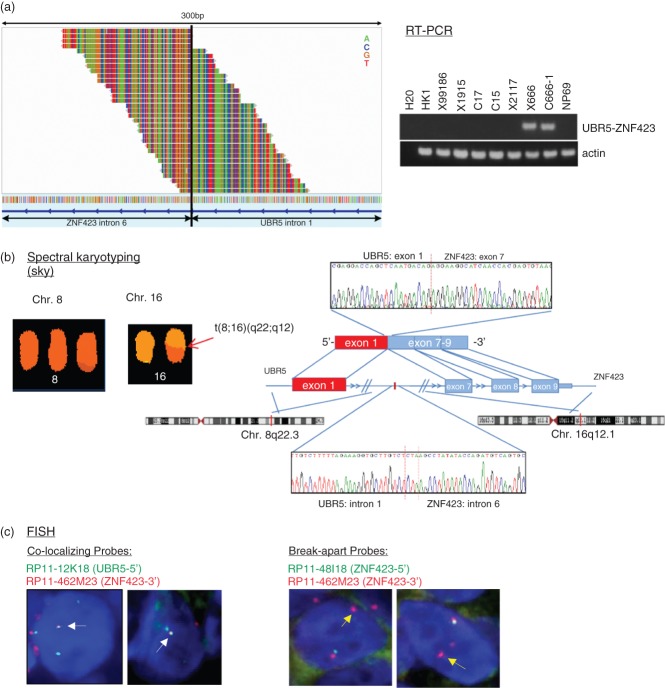
Figure 1.
Discovery of the UBR5–ZNF423 gene fusion in EBV-positive NPC. (a) By whole transcriptome sequencing and deFuse analysis, an UBR5–ZNF423 fusion transcript was identified in the NPC cell line C666-1. The spanning reads spanning the junction breakpoint within the UBR5–ZNF423 gene fusion are shown on the left. A spanning read is a read, one of whose end-sequences is aligned across the junction of the predicted fusion transcript. The UBR5–ZNF423 fusion transcripts in C666-1 and xeno-666 were confirmed by RT–PCR. The C666-1 cell line was derived from a NPC xenograft, xeno-666. (b) Direct sequencing confirmed that the chimeric transcripts contained the fusion of UBR5 exon 1 and ZNF423 exon7. Fusion junctions with respective exon numbers comprising the chimeric transcripts are indicated. The genomic fusion of UBR5 intron 1 on chromosome 8 and ZNF423 intron 6 on chromosome 16q was detected by direct DNA sequencing. Red bar indicates the 3 bp (CTA) microhomology region of the junction. Spectral karyotyping (SKY) analysis also showed the presence of a derivative chromosome, t(8; 16)(q22;q12), in C666-1. (c) The UBR5–ZNF423 fusion in C666-1 cells was validated by FISH analysis, using both break-apart and fusion probes. White arrows, fusion signal when co-localizing probes were used; yellow arrows, distinct red signal when break-apart probes were used.