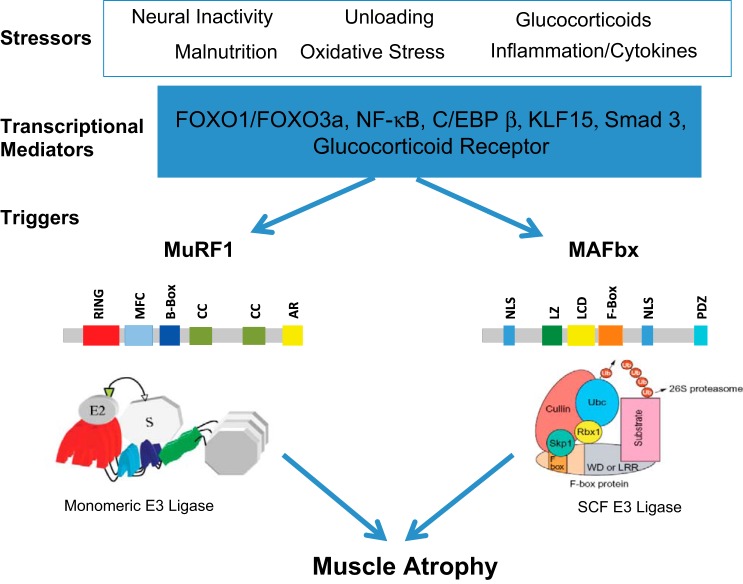
Fig. 1.
Regulation of muscle RING finger 1 (MuRF1) and muscle atrophy F-box (MAFbx) expression in skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscle atrophy is induced by a number of stressors, as illustrated here. These stressors can lead to the increase in the expression of a number of transcription factors, including the forkhead transcription factors (FOXO1 and FOX03a), NF-κB transcription factors (p65, c-Rel, RelB, p52, and p50), CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-β (C/EBPβ), kruppel-like factor-15 (KLF-15), and/or activation of the glucocorticoid receptor. These transcriptional mediators can bind to the promoter regions of either the MuRF1 or MAFbx genes, leading to an increase in their expression levels within the muscle. A schematic of the putative domain structure of each protein is shown. MuRF1 contains a RING finger domain (RING), a MuRF1 family conserved domain (MFC), a B-box domain (B-Box), coiled-coil domains (CC), and an acidic tail region (AR). MAFbx contains 2 nuclear localization signals (NLS), a leucine-zipper domain (LZ), a leucine-charged residue-rich domain (LCD), an F-box domain (F-box), and a PDZ domain (PDZ). SCF, Skp1-Cullin1-F-box protein.