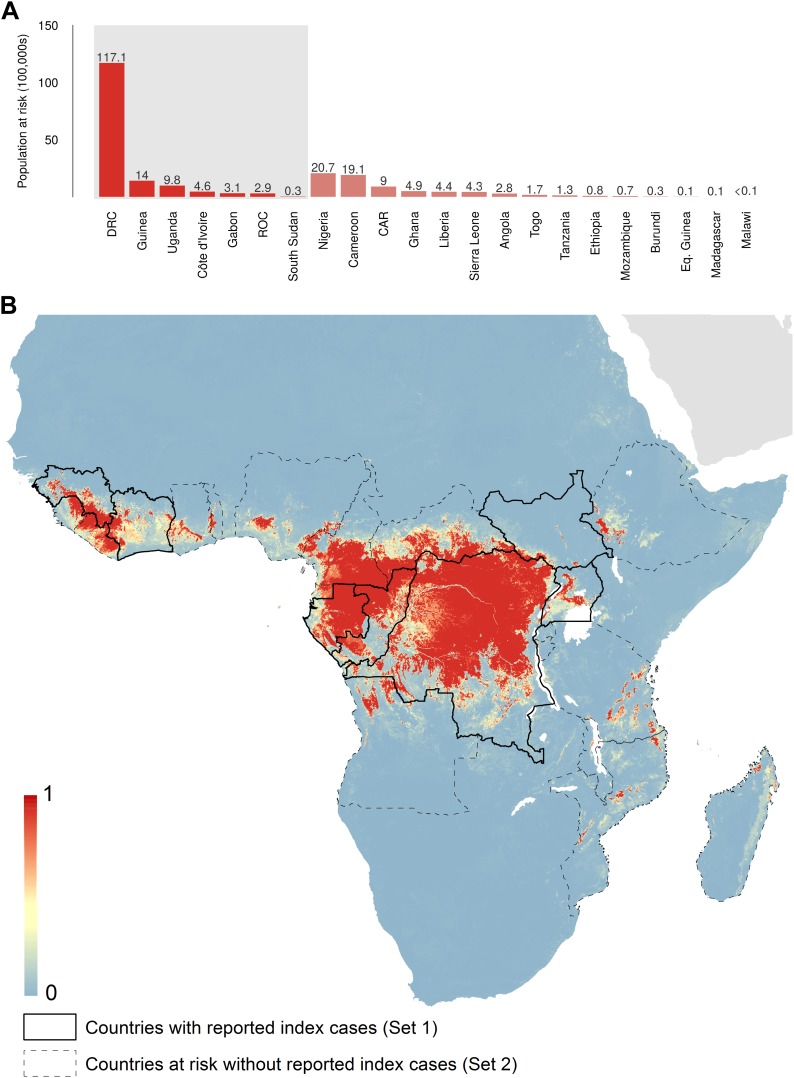
Figure 5. Predicted geographical distribution of the zoonotic niche for Ebola virus.
(A) Shows the total populations living in areas of risk of zoonotic transmission for each at-risk country. The grey rectangle highlights countries in which index cases of Ebola virus disease have been reported (Set 1); the remainder are countries in which risk of zoonotic transmission is predicted, but in which index cases of Ebola have not been reported (Set 2). These countries are ranked by population at risk within each set. The population at risk Figure in 100,000 s is given above each bar. (B) Shows the predicted distribution of zoonotic Ebola virus. The scale reflects the relative probability that zoonotic transmission of Ebola virus could occur at these locations; areas closer to 1 (red) are more likely to harbour zoonotic transmission than those closer to 0 (blue). Countries with borders outlined are those which are predicted to contain at-risk areas for zoonotic transmission based on a thresholding approach (see ‘Materials and methods’). The area under the curve statistic, calculated under a stringent 10-fold cross-validation procedure is 0.85 ± 0.04. Solid lines represent Set 1 whilst dashed lines delimit Set 2. Areas covered by major lakes have been masked white.