Fig. 2.
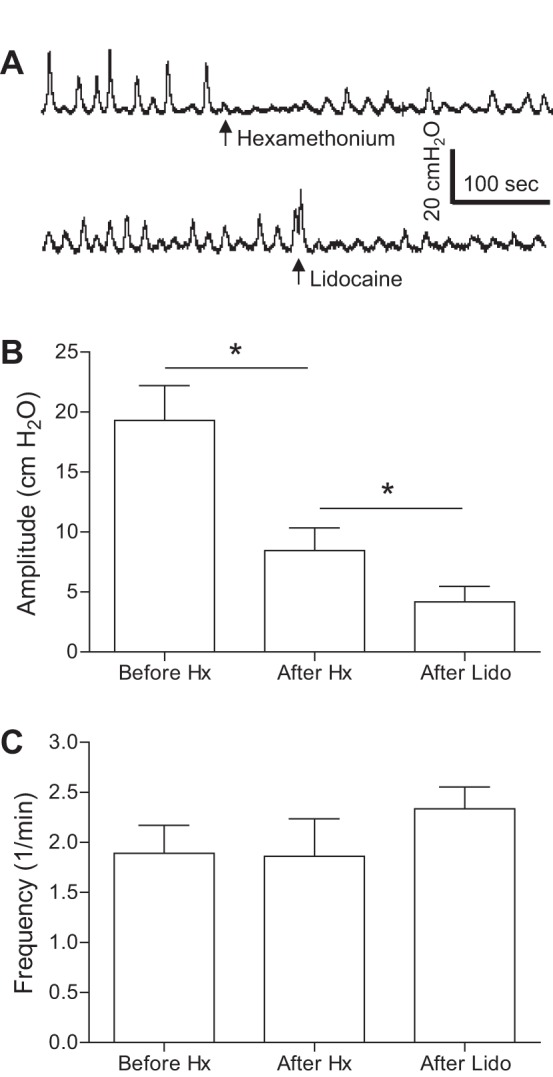
Spinal reflex bladder activity induced by bladder irritation using 0.25% AA after acute SCT at the T9/T10 level. A: under isovolumetric conditions, the maximal amplitude of rhythmic bladder contractions was significantly reduced by intravenous injection of 10 mg/kg hexamethonium (Hx). The contraction amplitude was further reduced by injection of 0.5 ml of 2% lidocaine (Lido) into the sacral S1 spinal cord. B: maximal contraction amplitude. C: contraction frequency. In total, seven cats were tested with Hx followed by Lido injection in four cats. *Significant difference (P < 0.01 by a paired Student's t-test).
