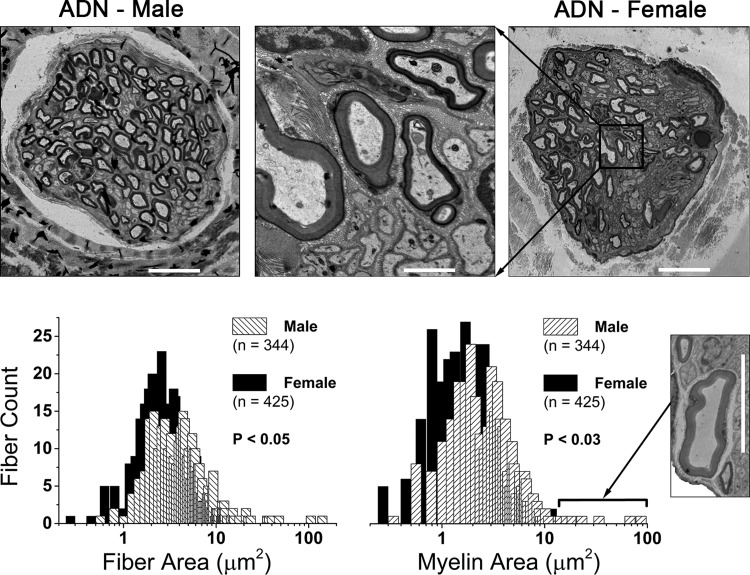
Fig. 1.
Sexual dimorphism in the myelination of rat aortic baroreceptor (BR) fibers. Top panels: electron microscopy images of the left aortic depressor nerve (ADN) from an adult male and female rat. Scale bars represent 10 μm and 1.5 μm for low and high (middle panel) magnification, respectively. Bottom panels: frequency distribution of fiber (axon + myelin) and myelin cross-sectional area (μm2). These two neuroanatomical features were the most significantly different across the populations of ADN myelinated fibers from female (n = 7) and male (n = 7) rats, with both measurements being significantly smaller in females. Bin centers increment in steps of 0.2 μm. Inset: several male nerve trunks contained at least one large myelinated BR fiber with axon and myelin area that were 5–10 times greater than population averages. Such large-diameter fibers were not observed in the ADN of female rats. Scale bar for inset is 10 μm.