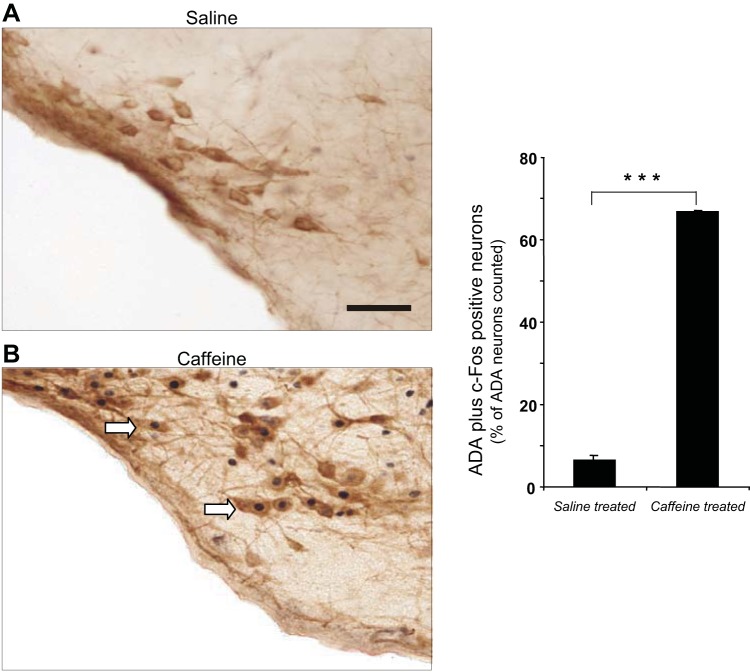
Fig. 6.
The posterior hypothalamus tuberomammillary nucleus (PH-TMN) showing double immunostaining of adenosine deaminase (ADA) and c-Fos. Caffeine-treated animals (B) showed an increase in the number of histamine (ADA) and c-Fos double-labeled neurons (indicated by arrows) compared with saline-treated controls (A). Left: the number of ADA plus c-Fos positive neurons is significantly higher in caffeine-treated animals (n = 4) compared with saline-treated controls (n = 3). All data are means ± SE. Scale bar = 60 μm. ***Significant difference by t-test (P < 0.0001).