Fig. 3.
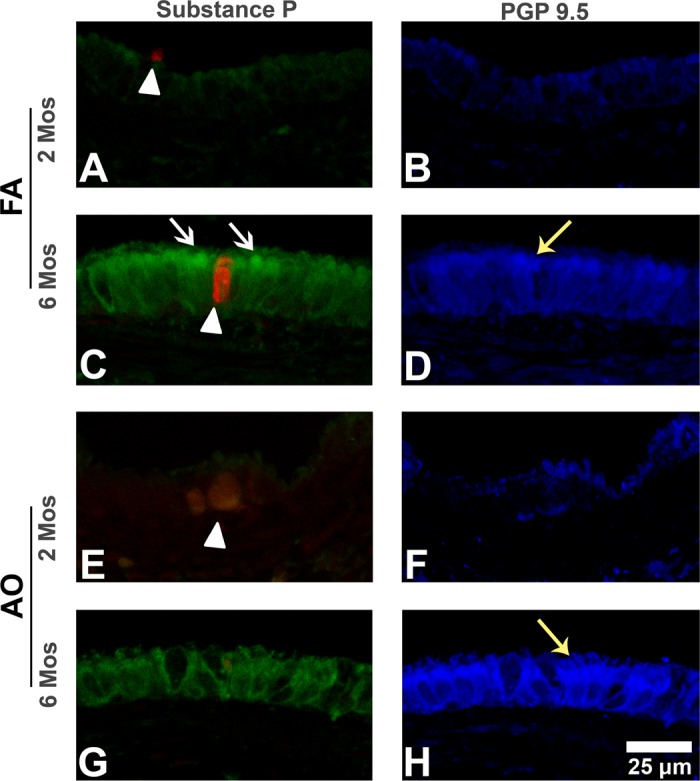
Substance P and protein gene product 9.5 immunohistochemistry (IHC) in midlevel airways. Representative micrographs of sections triple labeled with immunostains substance P (green stain; white arrows) and PGP 9.5 (blue stain; yellow arrows), and cell death marker EthD-1 (red stain; arrowheads) in midlevel airways from FA control 2-mo (A and B) and 6-mo (C and D) and AO-exposed 2 mo (E and F) and 6 mo (G and H) animals. Substance P epithelial peptide expression increases with age (A vs. C). Compared with FA (A, arrowhead), AO at 2 mo increases overall necrotic cell injury (E, arrowhead) but decreases epithelial PGP 9.5-immunopositive cells (B vs. F). At 6 mo, AO decreases substance P epithelial peptide expression (C vs. G, white arrows) and slightly increases epithelial PGP 9.5-immunopositive cells (D vs. H, yellow arrows). EAO images were similar to FA controls (not shown). Representative images selected from ∼4–6 slides/group. Scale bar = 25 μm.
