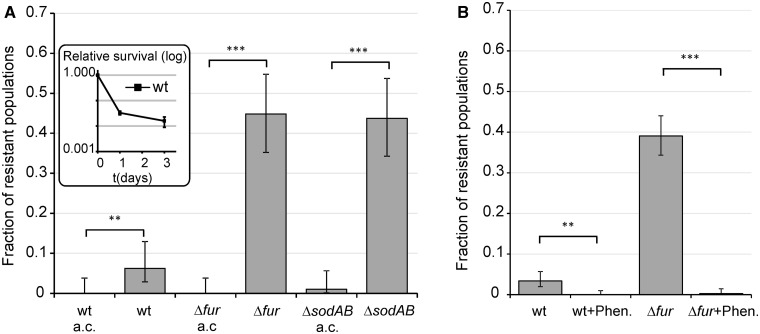
Fig. 5.
Effect of anaerobic conditions and iron chelation on ciprofloxacin-resistant evolution. (A) Effect of anaerobic conditions on the frequency of ciprofloxacin-resistant populations in the case of Δfur, ΔsodAB, and WT strains. Inlet in panel (A): Survival of the WT strain in the presence of ciprofloxacin under anaerobic conditions. Fractions are based on a total of n = 96 populations of each genotypes. (B) Effect of iron chelation using the cell permeable iron chelator o-phenantroline (50 µM) on the frequency of ciprofloxacin-resistant populations. Fractions are based on a total of n = 384 populations of each genotypes. Error bars represent confidence intervals of proportions (Wilson procedure). ***P ≤ 0.001, **P < 0.05 (chi-square test using the actual number of observations). a.c., anaerobic conditions; Phen., o-phenantroline.