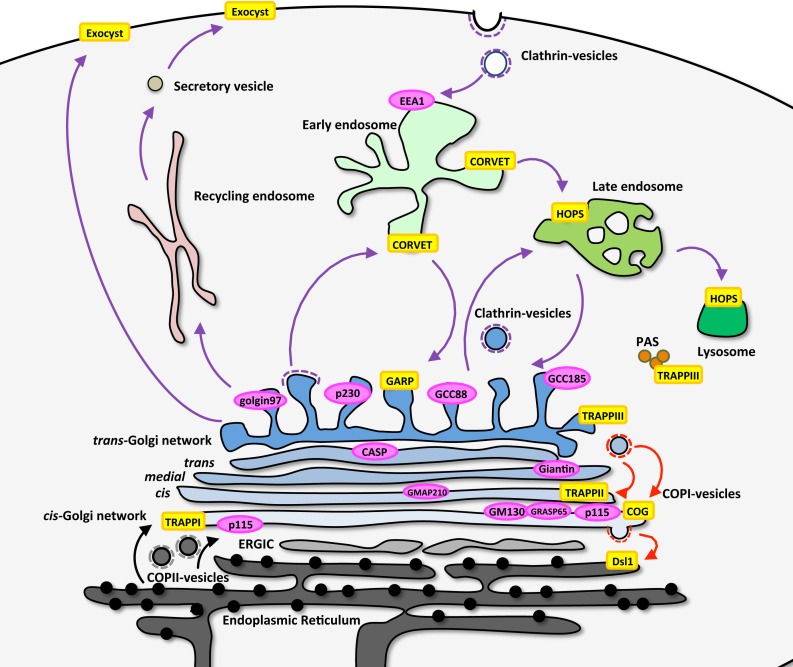
Figure 1. Location of membrane tethers in the trafficking pathways of the cells.
The location and identity of homodimeric coiled-coil tethers (pink ovals) and multiple subunit tethering complexes (yellow rectangles) are shown, as well as some of the transport pathways and transport vesicles that are regulated by the membrane tethers. The majority of the coiled-coil protein tethers are associated with the Golgi apparatus, whereas the multiple subunit tethering complexes are found throughout the secretory and endolysosomal pathways.
Abbreviations: CASP, CCAAT-displacement protein alternatively spliced product; COG, conserved oligomeric Golgi complex; CORVET, class C core vacuole/endosome tethering; EEA1, early endosome antigen-1; ERGIC, endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment; GARP, Golgi-associated retrograde protein complex; GMAP-210, Golgi microtubule-associated protein of 210 kDa; HOPS, homotypic fusion and vacuole protein sorting; PAS, phagophore assembly site; TRAPP, transport protein particle.