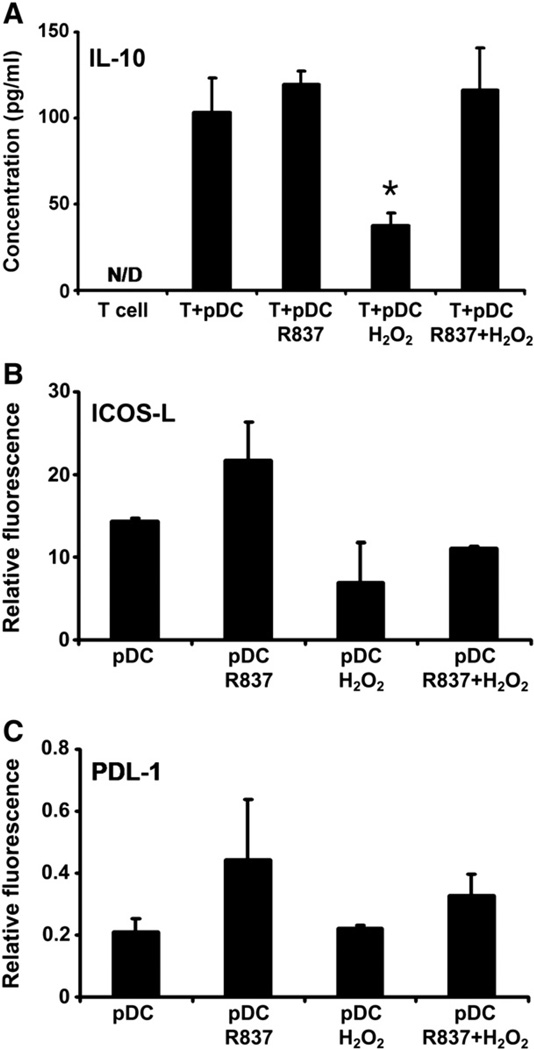
Fig. 5.
Effect of H2O2 treatment on the ability of pDCs to drive the differentiation of naïve autologous T lymphocytes toward IL-10-producing T cells. (A) Freshly isolated pDCs were treated with 0.01 µM H2O2 alone, R837 alone, or both together for 24 h and then washed and cocultured for up to 6 days with naïve autologous CD4+CD45RA+ T cells. Amounts of secreted IL-10 were determined in the culture supernatants by means of ELISA. (B and C) Expression of ICOS-L and PDL-1, promoters of the formation of regulatory T cells, on the surface of H2O2-exposed pDCs. Freshly isolated pDCs were stimulated with H2O2 and R837, separately and in combination, for 24 h and then stained for ICOS-L or PDL-1. Changes in the expression of tolerogenic cell-surface markers were analyzed using flow cytometry. Results are presented as means ± SE of three individual experiments. *P<0.05 vs T cells cocultured with untreated pDCs. N/D, not detectable.