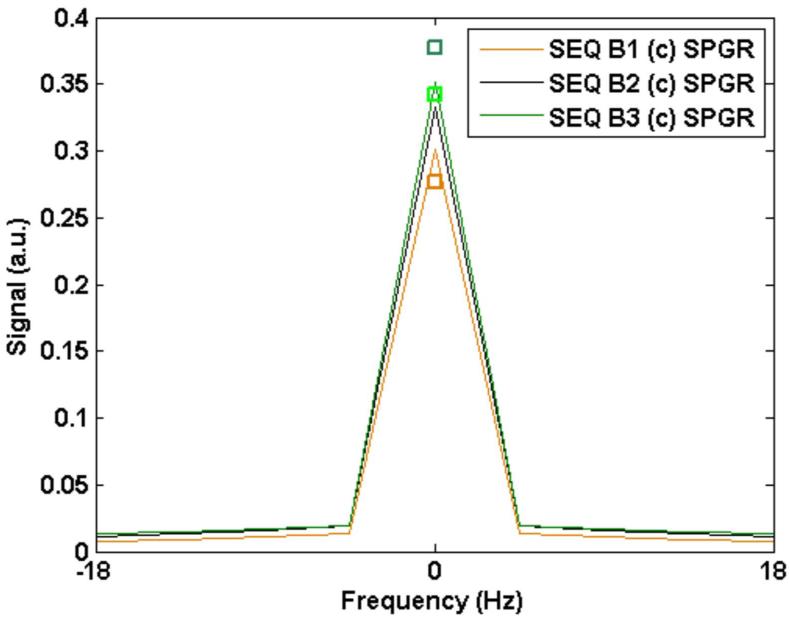
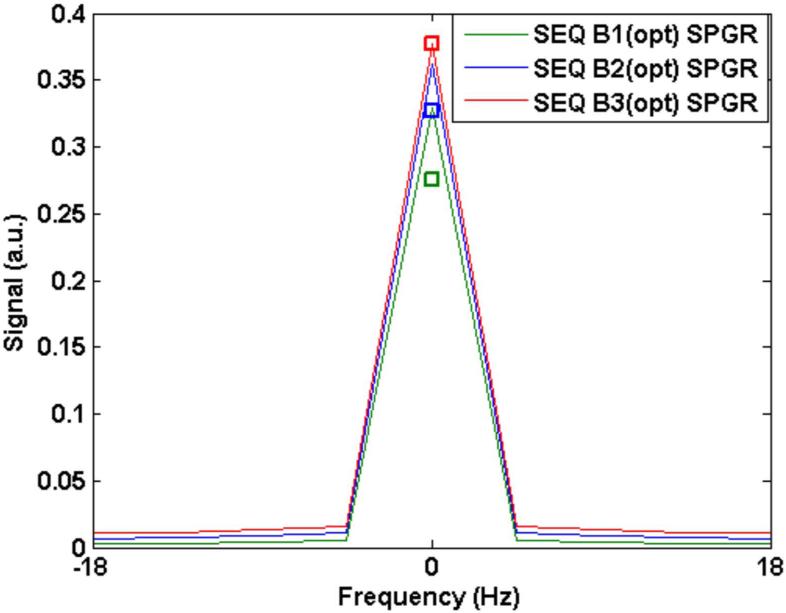
Figure 2.
A: The signal resulting from sequence B (SPGR) with an optimized flip angle scheme. Simulated signal from different TR times are shown: (B1): TR = 20 ms, flip = 45° (max); (B2) TR = 30 ms, flip = 50° (max); and (B3) TR = 40 ms, flip = 50° (max). The square boxes near the corresponding peaks mark measured SNR from the phantom scaled to the value obtained from the simulated signal for sequence B3(opt).
B: The signal resulting from sequence B (SPGR) with a constant flip angle scheme. Simulated signal from different TR times are shown: (B1): TR = 20 ms, flip = 35°; (B2) TR = 30 ms, flip = 40°; and (B3) TR = 40 ms, flip = 40°. The square boxes near the corresponding peaks mark measured SNR from the phantom normalized to the value obtained from the simulated signal for sequence B3.