Figure 1.
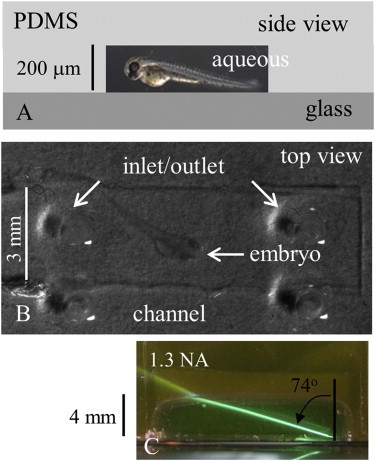
The PDMS microfluidic on a glass coverslip forming the zebrafish embryo confinement chamber. (A) Schematic side view of the chamber showing its aqueous, PDMS, and glass components and depth. (B) The actual device and confined embryo in top view as it would be imaged by the 2-P upright microscope objective. Inlet and outlet ports are for solution exchange. (C) A PDMS cube creates a cavity filled with an aqueous solution containing fluorescein, imitating the fish medium in a microfluidic channel. The HILO beam is created by an oil immersion objective (100×, 1.3 NA, and 200 μm working distance) and emerges into the aqueous side of the interface at ∼74°.
