Figure 5.
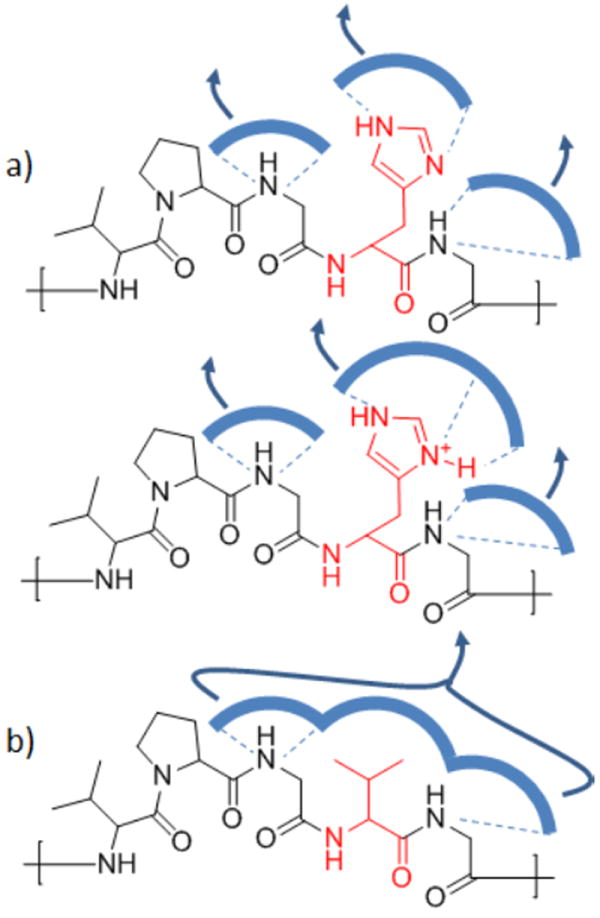
Sketch of the putative hydration for a) ELPs with protic guest-residue side chains (red) and b) with aprotic guest residue side chains (red). In a) the hydration layer of the protic guestresidue side chain is individually stabilized by H-bonds and can vanish independently (decoupled) from backbone hydration layers. When the His residues are charged (a) bottom) the individual (decoupled) side chain hydration layers are even more stable than in the charge neutral analogue (a) top). The higher stability is schematically depicted as larger hydration shell and larger number of H-bonds. In b) the hydration layer of the guest-residue side chain is stabilized via coupling to neighboring backbone hydration layers and hence dehydration takes place cooperatively.
