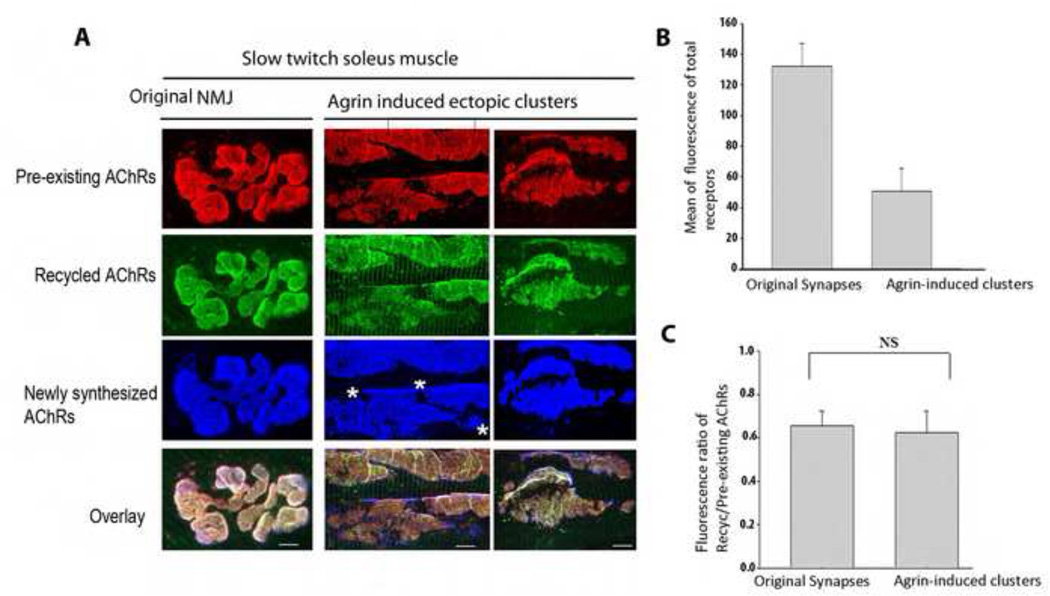
Figure 1.
Identification of a recycled receptor pool at ectopic agrin-induced acetylcholine receptor clusters in the Soleus muscles of adult rats. A) Examples of agrin-induced ectopic clusters and receptors at the postsynaptic membrane of a NMJ. Note the existence of all three receptor pools (recycled, pre-existing and newly synthesized) at both ectopic and the original NMJ. B) Graph summarizing the quantification of postsynaptic receptor density at agrin-induced clusters (N=18) and original NMJs (N=14). C) Graph summarizing the quantification of fluorescence ratio between the recycled AChR and pre-existing AChRs at agrin-induced and original synaptic clusters (as illustrated in panel A). Note that there is no significant difference between the size of the recycled receptor pool in agrin-induced clusters (N=24) and original NMJs (N=23) (Student test p=0.24), indicating unchanged internalization rates. Bar graph (±s.d). Images in A have been adjusted in Photoshop (Adobe) to maximize contrast. Bars, 10 µm. * indicates where newly synthesized AChRs are inserted. At least three rats were used in each experiment.