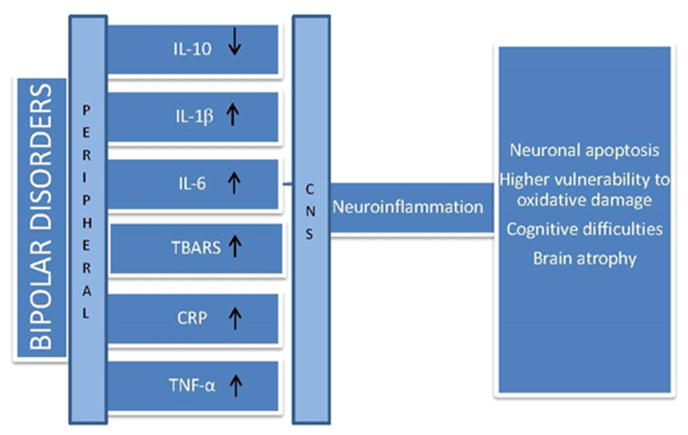
Figure 1.
Bipolar disorders are characterized by elevated levels of peripheral pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukins (IL-6, IL-2R, IL-1beta), tumour necrosis factor (TNF-α) and oxidative stress (Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances -TBARS and C-reactive protein - CRP). Pro-inflammatory agents enter the central nervous system (CNS) via the blood brain barrier, activate the brain inflammatory signal and release inflammatory agents, monocytes and macrophages in the brain. Exposure to pro-inflammatory substances and reactive oxidative substances is associated with neuronal damage and loss of brain function.