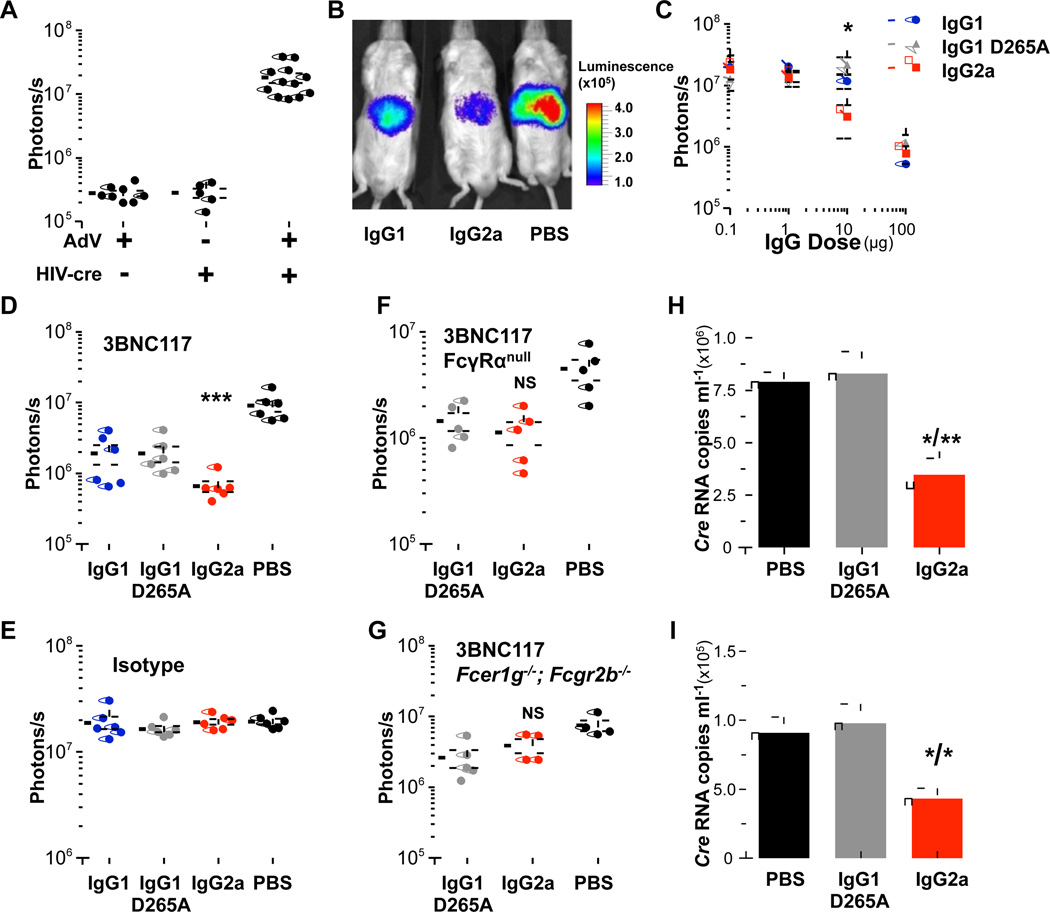
Figure 2. Mouse IgG2a subclass variants of 3BNC117 exhibit improved in vivo activity.
The in vivo activity of mouse-human chimeric Fc variants of 3BNC117 was assessed in a mouse model for HIV entry (Pietzsch et al., 2012) using luciferase reporter mice. (A) Infection with HIV-1YU-2 Cre pseudovirus was accomplished by adenoviral-mediated expression of human CD4 and CCR5. (B-D) Enhanced in vivo activity was observed for mouse IgG2a subclass variants of 3BNC117, compared to mouse IgG1 and mouse IgG1 D265A (B: representative in vivo luminescence image; C: 3BNC117 variants administered at different doses (0.1–100 µg/ml, i.p.), data are presented as the mean ± SEM, n=5/group, *p<0.05 mouse IgG2a vs. mouse IgG1 D265A; D: 3BNC117 administered at a single concentration (50 µg, i.p.) n=5–6/group, ***p<0.001 compared to PBS-treated group. (E) Isotype subclass variants of a non-HIV-1 reactive mAb (mGO53, 500 µg) displayed no protective activity, n=5–6/group. (F-G) No significant difference in the in vivo activity was observed between mouse IgG2a and mouse IgG1 D265A (FcγR null binding) variants of 3BNC117 (50 µg, i.p.) in two strains of FcγR deficient mice (FFcγRα null;GFcer1g−/−; Fcgr2b−/−) NS: not significant mouse IgG2a vs. PBS or mouse IgG1 D265A. (H–I) Enhanced in vivo activity of mouse IgG2a 3BNC117 was accompanied by improved virus clearance. Serum pseudovirus content (1 (H) and 3 (I) days following HIV-1YU-2 Cre pseudovirus infection) was determined using a qRT-PCR-based assay specific for Cre. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p<0.05; **p<0.01 compared to PBS/mIgG1 D265A groups; n=4 mice/group.