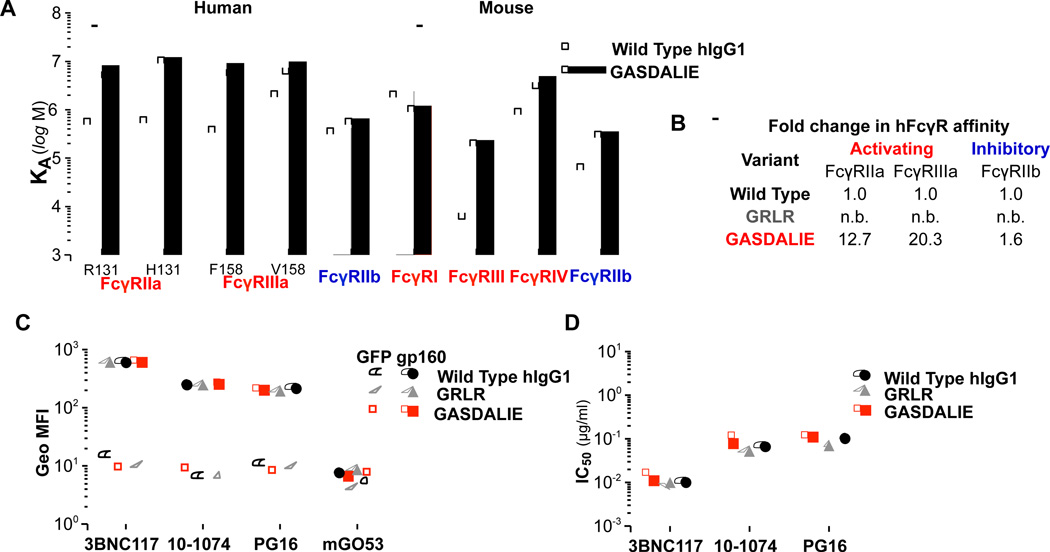
Figure 4. Generation and characterization of Fc domain variants of anti-HIV-1 mAbs with selective FcγR binding capacity.
Fc domain variants (GRLR and GASDALIE) of hIgG1 anti-HIV-1 mAbs with differential FcγR affinity (A–B; see also Table S4 (A: IgG Fc domain variant affinity against different classes and common allelic variants of human and mouse FcγRs; B: Fold enhancement in the affinity of Fc domain variants compared to wild-type human IgG1 for human FcγRs. n.b.: no binding)) were generated and characterized in terms of (C) antigen specificity (see also related Figure S3) and (D) in vitro neutralization activity. (C) Binding of anti-HIV-1 mAb hIgG1 Fc domain variants to gp160ΔctYU-2- or GFP-expressing HEK293T cells was assessed by flow cytometry. Data represent the geometric mean fluorescence intensity (Geo MFI) from three independent experiments. (D) In vitro neutralization activity (against HIV-1YU-2) of human Fc domain variants of anti-HIV-1 mAbs was determined by a standardized TZM-bl assay (Montefiori, 2005)(see also Tables S5 and S6).