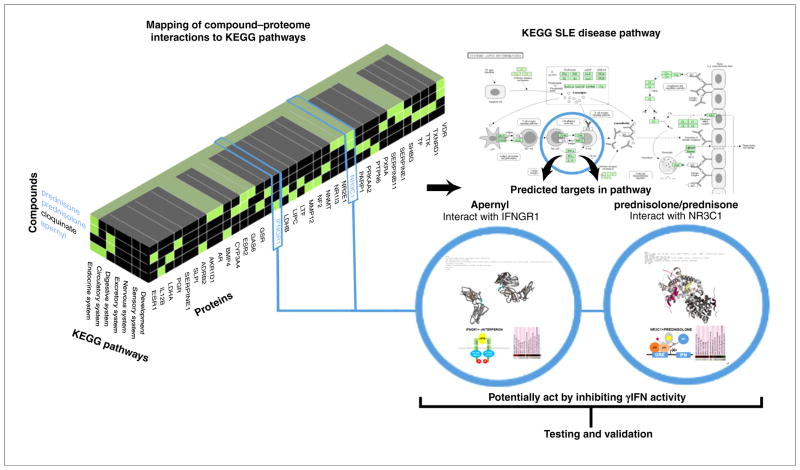
FIGURE 4.
Multiscale modeling of complex molecular, cellular, and physiological systems using Computational Analysis of Novel Drug Opportunities (CANDO) for application in medicine. Proteins with high interaction scores for the top predicted CANDO compounds are mapped against KEGG human pathways and analyzed for possible mechanisms and/or context of action. For illustrative purposes, the interactions of apernyl with interferon gamma receptor 1 (IFNGR1) and the corticoid drugs prednisolone and prednisone with glucocorticoid receptor (NR3C1) are considered above. Mapping of predicted CANDO molecular interaction signatures to KEGG pathways revels that both compounds interact with proteins involved with γinterferon (γIFN) regulation, and might have a role in the systemic lupus erythematous (SLE) disease pathway. Moreover, these compounds might have inhibitory activity via distinct mechanisms with apernyl acting to block γIFN activity by potentially interfering with γIFN binding to its cognate receptor, whereas prednisolone and/or prednisone might act by suppressing γIFN gene transcription via the glucocorticoid transrepression mechanism. The two compounds are well-known drugs that are used in the treatment of SLE, indicating CANDO results representing a retrospective prediction. However, given that the CONTEXTUALIZATION process of the CANDO platform suggests heretofore unknown mechanisms of action by combining publically available structural, regulatory and expression information, the power of this approach, which is pathway agnostic with regards to mechanism of action, strongly points towards specific lines of testing and validation of multiple mechanisms of action of putative drugs to treat an indication.