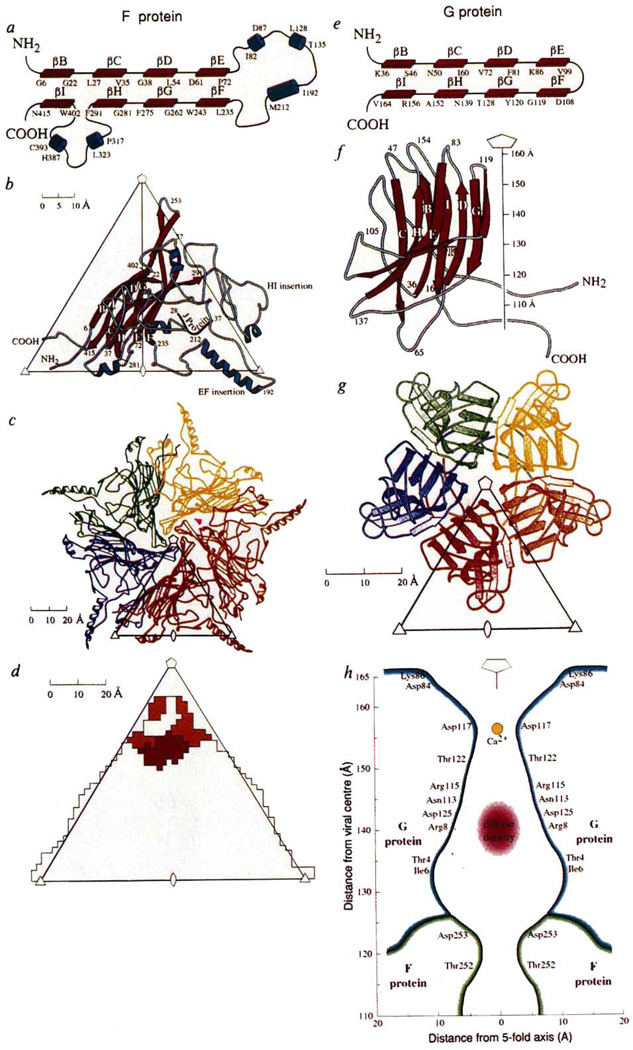
FIG. 2.
Structure of the viral proteins G and F. a, e, Topological depiction. The antiparallel sheet is subsequently wound into a right-handed helix to make a β barrel, b, f, Ribbon diagrams showing secondary structure nomenclature and amino-acid numbering. The orientation of the F protein is shown, viewed down a 2-fold axis, relative to an icosahedral asymmetric unit formed by adjacent 5-, 3- and 2-fold axes, whereas the G protein is shown as a side view with the spike pointing along the 5-fold axis. c, g, 9S and 6S pentameric units of the F and G proteins, respectively, viewed down a 5-fold axis. d, Footprint of the spike onto the F protein. The colours indicate different sub-units of G corresponding to the code shown in g. h, Cross-section through the spike showing the amino acids that line the hydrophilic channel. The larger diffuse density may be part of the H protein and a smaller density on the 5-fold axis is a putative Ca2+ ion.