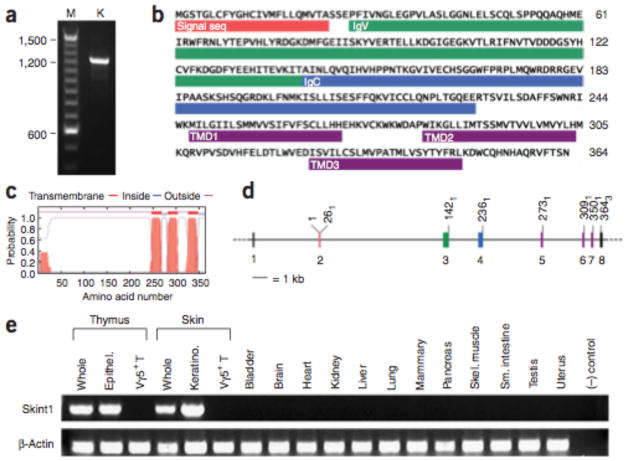
Figure 3.
Skint1 gene and protein structure. (a) Amplification of the full-length coding region of Skint1 from keratinocyte cDNA. The DNA sequence reveals a consensus Kozak sequence for translation initiation and a continuous open reading frame of 364 amino acids (Supplementary Fig. 2). (b) Deduced amino acid sequence of Skint1. The locations of the signal sequence, IgV, IgC and transmembrane domains (TMDs) are indicated. (c) Hydropathy plot from the TMHMM program predicts three TMDs with high probability, yielding an extracellular N terminus and cytoplasmic C terminus. (d) Alignment of cDNA with genomic DNA reveals that Skint1 is encoded in modular exons. Exon colors correspond to those of the encoded domains shown in b. The codon position of the last base of each exon is indicated. (e) Tissue distribution of Skint1 expression. Products of RT-PCR with Skint1-specific primers visualized on an agarose ge (Skint1); Actb amplification is shown as a control (b-Actin). Thymic epithelium and Vγ5+ T cell RNAs were obtained at E15–16; RNAs from all other tissues were obtained at adulthood. Skint1 expression is detected in whole thymus and thymic epithelium and in whole skin and keratinocyte.