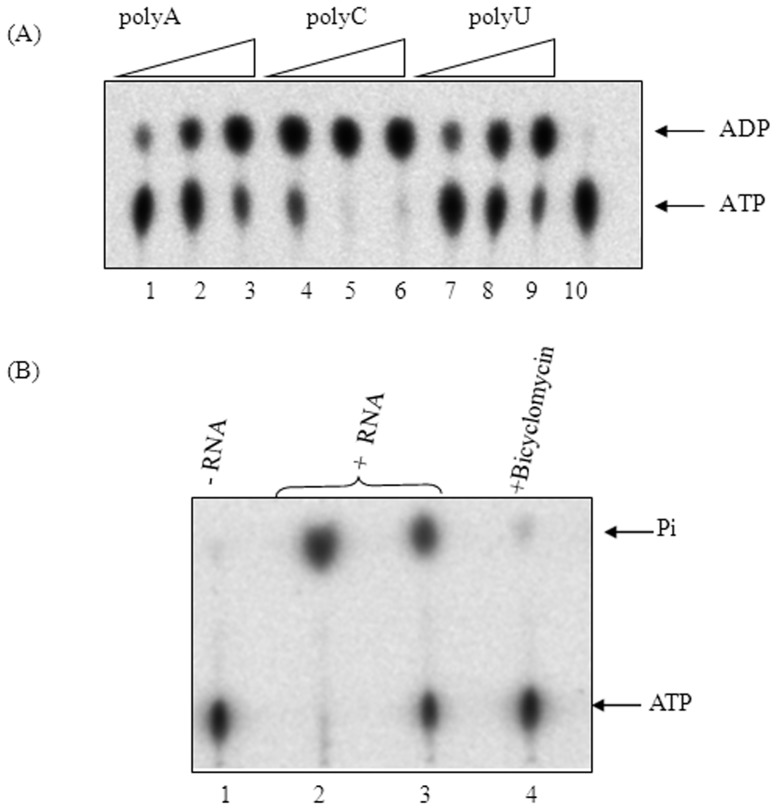
Figure 1. ATPase activity of MtbRho.
(A) MtbRho hydrolyses ATP in presence of increasing concentrations of homopolymeric RNA – polyA (lanes1–3), polyC (lanes4–6) and polyU (lanes 7–9). No hydrolysis was observed in absence of RNA (lane 10). (B) MtbRho hydrolyzes ATP in presence of mycobacterial RNA. No hydrolysis was observed in absence of RNA (lane 1); 2 and 1 µg of M. smegmatis RNA stimulated ATP hydrolysis (lanes 2,3); the reaction is inhibited by Bicyclomycin (lane 4). ATPase assay was carried out as described in Methods. [1 mM unlabeled ATP was used as substrate, along with 100 nCi of α-32P-ATP (Panel A) or 100 nCi of γ-32P-ATP(Panel B), as tracer. Hydrolysis resulted in formation of α-32P-ADP (Panel A) or 32Pi (Panel B) which were visualized using phosphorimager].