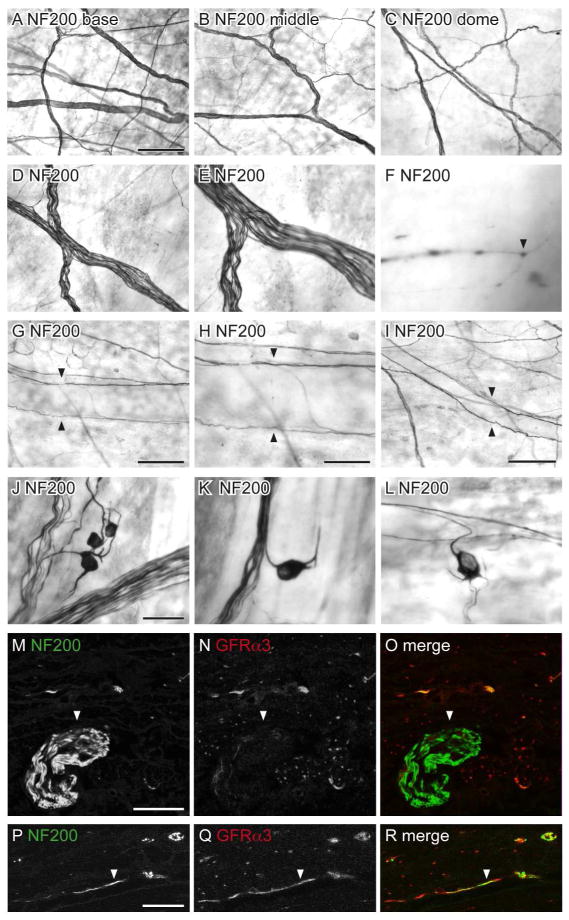
Figure 10.
Distribution of NF200-immunoreactive (IR) axons in the bladder. Panels A–L show DAB-processed whole mounts viewed with conventional microscopy whereas M–R are confocal micrographs of immunofluorescence in cryosections. A–C: Many NF200-IR axons were found in the detrusor and were distributed evenly throughout the bladder (a: base; b: middle; c: dome). D–E: The majority of NF200-IR axons travelled in large diameter axon bundles. F: NF200-IR terminals were occasionally observed in the detrusor (arrowhead). G–I: Few NF200-IR axons were associated with the vasculature; these were para-vascular (arrowheads) and only observed on primary (G, H) and secondary (I) vascular branches. J–L: NF200-IR neurons were observed in the detrusor; many had short processes and were found individually (K, L) or in small clusters (J). M–O: Large diameter NF200-IR axon bundles (arrowheads) on the serosal surface were not immunoreactive for GFRα3. P–R: Some NF200-IR axons in the detrusor were immunoreactive for GFRα3 (arrowheads); it was difficult to determine if these comprised single or multiple axons. The serosal surface of the bladder is orientated to the bottom in panels m–r. Scale bar = 200 μm in (A) also applies to (B, C); 100 μm in (D) also applies to (E); 20 μm in (F); 200 μm in (G); 100 μm in (G); 200 μm in (I), 50 μm in (J) also applies to (K, L); 20 μm in (M) also applies to (N, O); 10 μm in (P) also applies (Q, R). GFRα3, glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family receptor α3; NF200, neurofilament, 200 kDa.